Page 169 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 169
Replacement structure for the answer to question 2 in Chapter 2.9 (Aripiprazole)
Alkyl (aliphatic) chain
(Lipid soluble)
Ether oxygen
(Water soluble)
Amide
Halogens
(Water soluble)
(Lipid soluble)
of bicyclic ring
(Lipid soluble)
Aromatic (phenyl) ring
(Lipid soluble)
Aripiprazole Hydrocarbon portion
Alkyl (aliphatic) chain
(Lipid soluble)
158 Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
Replacement structure for question 6 in BOTH Chapters 1.12 and 2.12 (Chlorpropamide and Other
Sulfonylureas)
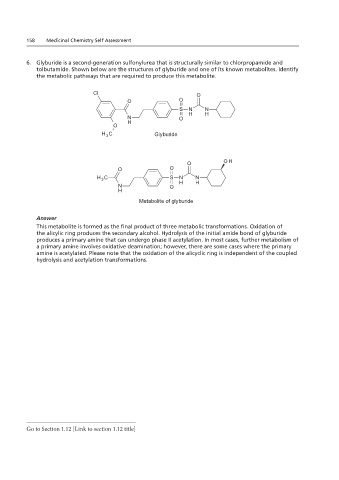
6. Glyburide is a second-generation sulfonylurea that is structurally similar to chlorpropamide and
tolbutamide. Shown below are the structures of glyburide and one of its known metabolites. Identify
the metabolic pathways that are required to produce this metabolite.
Cl O
O O
S N N
N O H H
O H
H 3 C Glyburide
O OH
O O
H 3 C S N N
N O H H
H
Metabolite of glyburide
Answer
This metabolite is formed as the final product of three metabolic transformations. Oxidation of
the alicylic ring produces the secondary alcohol. Hydrolysis of the initial amide bond of glyburide
produces a primary amine that can undergo phase II acetylation. In most cases, further metabolism of
a primary amine involves oxidative deamination; however, there are some cases where the primary
amine is acetylated. Please note that the oxidation of the alicyclic ring is independent of the coupled
hydrolysis and acetylation transformations.
Go to Section 1.12 [Link to section 1.12 title]