Page 172 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 172
2.13 Dabigatran Etexilate 161
Chapters 1.13/2.13 (removed bolded text)
A B E F
D
C
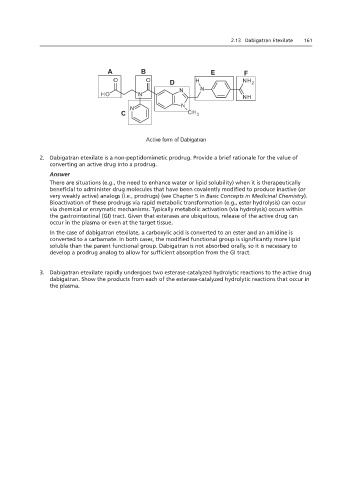
Active form of Dabigatran
2. Dabigatran etexilate is a non-peptidomimetic prodrug. Provide a brief rationale for the value of
converting an active drug into a prodrug.
Chapters 1.13/2.13 (removed bold drug name)
Answer
There are situations (e.g., the need to enhance water or lipid solubility) when it is therapeutically
beneficial to administer drug molecules that have been covalently modified to produce inactive (or
very weakly active) analogs (i.e., prodrugs) (see Chapter 5 in Basic Concepts in Medicinal Chemistry).
Bioactivation of these prodrugs via rapid metabolic transformation (e.g., ester hydrolysis) can occur
via chemical or enzymatic mechanisms. Typically metabolic activation (via hydrolysis) occurs within
the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Given that esterases are ubiquitous, release of the active drug can
occur in the plasma or even at the target tissue.
In the case of dabigatran etexilate, a carboxylic acid is converted to an ester and an amidine is
converted to a carbamate. In both cases, the modified functional group is significantly more lipid
soluble than the parent functional group. Dabigatran is not absorbed orally, so it is necessary to
develop a prodrug analog to allow for sufficient absorption from the GI tract.
3. Dabigatran etexilate rapidly undergoes two esterase-catalyzed hydrolytic reactions to the active drug
Dabigatran etexilate mesylate
dabigatran. Show the products from each of the esterase-catalyzed hydrolytic reactions that occur in
the plasma.