Page 177 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 177
1.14 and 2.14 (drug name – remove bold)
1.14 and 2.14 (drug name – remove bold)
166 Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
Continued from previous page.
Fenofibrate Gemfibrozil
C Aromatic Hydrophobic Neutral Absorption Hydrophobic None
hydrocarbon Fenofibrate Gemfibrozil
van der Waals
Letter “C” – add bold
π-π Stacking
Letter “C” – add bold Hydrophilic (O) Neutral Solubility (O) H-bonding (A) Ser, Thr, Tyr, Cys, Asn, Gln,
D
Ether
Hydrophobic (R) Absorption (R) Dipole–dipole His, Trp
Ion–dipole (as the
dipole)
E Aliphatic Hydrophobic Neutral Absorption Hydrophobic None
alkane van der Waals
F Ester Hydrophilic Neutral Solubility (COO) H-bonding (A) Ser, Thr, Tyr, Cys, Asn, Gln,
C
(COO) Absorption (R) Dipole–dipole His, Trp
C
Hydrophobic (R) Ion–dipole (as the
2.14 – remove bold from label dipole)
.
2.14 – remove bold from label
B
F
B F D
A C
A C D
E
E Fenofibrate
Fenofibrate
2.14 – remove bold from label
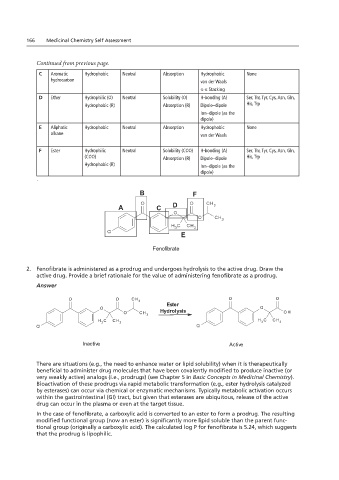
2. Fenofibrate is administered as a prodrug and undergoes hydrolysis to the active drug. Draw the
active drug. Provide a brief rationale for the value of administering fenofibrate as a prodrug.
2.14 – remove bold from label
Answer
O O CH 3 Ester O O
O O CH 3 O O Hydrolysis O O OH
Ester O CH 3
O Hydrolysis 3 O OH H 3 C CH 3
CH
C
H
3
Cl O CH 3 Cl
H 3 C CH 3 H 3 C CH 3
Cl Cl
Inactive Active
Inactive Active
There are situations (e.g., the need to enhance water or lipid solubility) when it is therapeutically
beneficial to administer drug molecules that have been covalently modified to produce inactive (or
very weakly active) analogs (i.e., prodrugs) (see Chapter 5 in Basic Concepts in Medicinal Chemistry).
Bioactivation of these prodrugs via rapid metabolic transformation (e.g., ester hydrolysis catalyzed
by esterases) can occur via chemical or enzymatic mechanisms. Typically metabolic activation occurs
within the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, but given that esterases are ubiquitous, release of the active
drug can occur in the plasma or even at the target tissue.
In the case of fenofibrate, a carboxylic acid is converted to an ester to form a prodrug. The resulting
modified functional group (now an ester) is significantly more lipid soluble than the parent func-
tional group (originally a carboxylic acid). The calculated log P for fenofibrate is 5.24, which suggests
that the prodrug is lipophilic.