Page 174 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 174
2.13 Dabigatran Etexilate 163
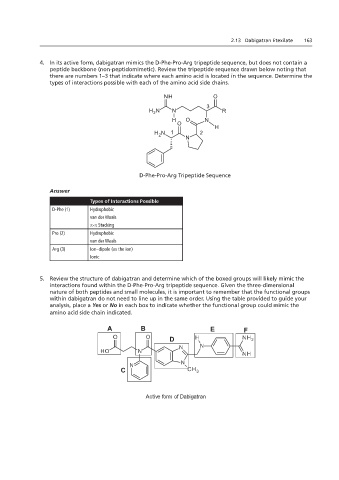
4. In its active form, dabigatran mimics the D-Phe-Pro-Arg tripeptide sequence, but does not contain a
peptide backbone (non-peptidomimetic). Review the tripeptide sequence drawn below noting that
there are numbers 1–3 that indicate where each amino acid is located in the sequence. Determine the
4. In its active form, dabigatran mimics the D-Phe-Pro-Arg tripeptide chains.
types of interactions possible with each of the amino acid side chains.
NH O
3
H 2 N N R
H O N
O H
H N 1 2
2
N
D-Phe-Pro-Arg Tripeptide Sequence
D-Phe-Pro-Arg Tripeptide Sequence
Answer
Types of Interactions Possible
5. Review side chain indicated.
D-Phe (1) Hydrophobic
van der Waals
π-π Stacking
A
Pro (2) Hydrophobic B E F
van der Waals O O D H NH 2
Arg (3) Ion–dipole (as the ion) N N
Ionic H O N NH
N
N
C CH 3
5. Review the structure of dabigatran and determine which of the boxed groups will likely mimic the
interactions found within the D-Phe-Pro-Arg tripeptide sequence. Given the three-dimensional
nature of both peptides and small molecules, it is important to remember that the functional groups
Active form of Dabigatran
within dabigatran do not need to line up in the same order. Using the table provided to guide your
Chapter 2.13 (remove bolded drug name)
analysis, place a Yes or No in each box to indicate whether the functional group could mimic the
amino acid side chain indicated.
6. Dabigatran salt. Provide a brief rationale for the value of administering the salt form of a drug.
A B E F
D
C
Active form of Dabigatran
Dabigatran etexilate mesylate