Page 178 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 178
2.14 Fenofibrate and Gemfibrozil 167
3. The calculated log P for fenofibrate is 5.24, whereas the calculated log P for gemfibrozil is 3.9.
1.14 and 2.14 (drug name – remove bold)
Provide a structural rationale for the difference in this pharmacokinetic property.
Fenofibrate Gemfibrozil
3. The calculated for difference in this pharmacokinetic property.
Answer Letter “C” – add bold
A larger calculated log P value reflects the presence of additional hydrophobic character. Let’s see
if that statement pans out as we evaluate each of these molecules. The structure evaluation grid
for fenofibrate reveals that there are several functional groups that contribute to its hydrophobic
character including the halogenated aromatic hydrocarbon, the aromatic hydrocarbon, and both
aliphatic alkanes. Evaluation of gemfibrozil reveals hydrophobic character from a dimethyl substi-
tuted aromatic hydrocarbon and an aliphatic alkane. The larger calculated log P value for fenofibrate
is justified by the presence of significantly more functional groups with hydrophobic character.
Gemfibrozil
Fenofibrate
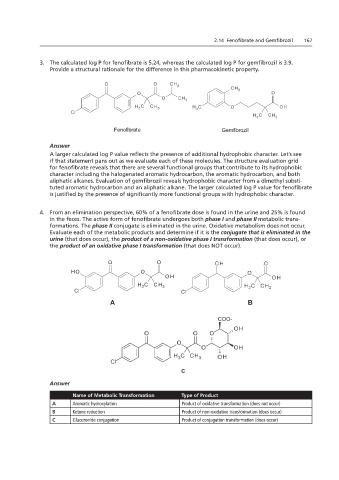
4. From an elimination perspective, 60% of a fenofibrate dose is found in the urine and 25% is found
C
1.14 and 2.14 (drug name – remove bold)
in the feces. The active form of fenofibrate undergoes both phase I and phase II metabolic trans-
formations. The phase II conjugate is eliminated in the urine. Oxidative metabolism does not occur.
Evaluate each of the metabolic products and determine if it is the conjugate that is eliminated in the
4. From an elimination NOT occur).
2.14 – remove bold from label
urine (that does occur), the product of a non-oxidative phase I transformation (that does occur), or
the product of an oxidative phase I transformation (that does NOT occur).
B F
O O
H O A C D O
OH
Fenofibrate
H 3 C CH 3 Gemfibrozil
Cl
E
A
Letter “C” – add bold B
Fenofibrate
2.14 – remove bold from label
O O CH 3 O O
Ester
O Hydrolysis O
O CH 3 OH
H 3 C CH 3 C C H 3 C CH 3
Cl Cl
Answer
2.14 – remove bold from label
Inactive
5. Provide a structural rationale for why oxidative O-dealkylation does not occur. Active
Name of Metabolic Transformation
Type of Product
A Aromatic hydroxylation Product of oxidative transformation (does not occur)
Answer:
F
B Ketone reduction B Product of non-oxidative transformation (does occur)
C Glucuronide conjugation D Product of conjugation transformation (does occur)
A C
1 2
E
Fenofibrate
2.14 – remove bold from label
O O CH 3 O O
Ester
O Hydrolysis O
O CH 3 OH
H 3 C CH 3 H 3 C CH 3
Cl Cl
Inactive Active