Page 247 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 247
4. Zanamivir exerts its his, provide an explanation how zanamivir inhibits neuraminidase.
Glycosidic bond
N-Acetylsialic acid bound to glycoprotein
Zanamivir
Answer:
Zanamivir is a stable a cleavable glycosidic bond.
Structurally identical
to N-acetylsialic acid
(with exception of
the double bond)
Zanamivir Lacks glycosidic bond
5. Shown below is a activity is likely to be more active, less active, or similar to that of zanamivir?
236 Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
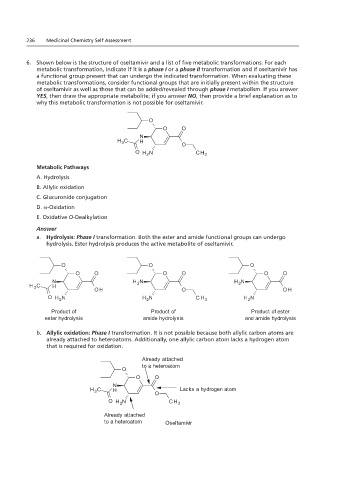
6. Shown below is the structure of oseltamivir and a list of five metabolic transformations. For each
Chapter 2.27
metabolic transformation, indicate if it is a phase I or a phase II transformation and if oseltamivir has
a functional group present that can undergo the indicated transformation. When evaluating these
Please replace the structure for the answer of Q1 with the one below.
metabolic transformations, consider functional groups that are initially present within the structure
of oseltamivir as well as those that can be added/revealed through phase I metabolism. If you answer
YES, then draw the appropriate metabolite; if you answer NO, then provide a brief explanation as to
why this metabolic transformation is not possible for oseltamivir.
6. Shown below is the structure of for oseltamivir
Carboxylic acid (Acidic functional group)
Normal pH range = 2.5 to 5
Would be primarily ionized at a pH = 7.2
Metabolic Pathways
A. Hydrolysis Guanidine (Basic functional group)
B. Allylic oxidation Normal pH range = 12 to 13
Would be primarily ionized at a pH = 7.2
C. Glucuronide conjugation
D. ω-Oxidation
E. Oxidative O-Dealkylation
Answer
Answer:
Please replace the structure for the answer to Q6, part a with the one below (page 4, middle structure)
a. Hydrolysis: Phase I transformation. Both the ester and amide functional groups can undergo
A. Hydrolysis: Phase I oseltamivir.
hydrolysis. Ester hydrolysis produces the active metabolite of oseltamivir.
Product of Product of Product of ester
Ester hydrolysis
Ester and amide
Amide hydrolysis
ester hydrolysis amide hydrolysis and amide hydrolysis
hydrolysis
b. Allylic oxidation: Phase I transformation. It is not possible because both allylic carbon atoms are
B. Allylic oxidation: Phase a hydrogen atom that is required for oxidation.
already attached to heteroatoms. Additionally, one allylic carbon atom lacks a hydrogen atom
that is required for oxidation.
Already attached
to a heteroatom
Lacks a hydrogen atom
Already attached
to a heteroatom Oseltamivir
C. Glucuronide conjugation: Phase II.