Page 125 - PG 504-theoretical notes-phyto-1-2024-2025..
P. 125
Clinical pharmacy PharmD program Third level Phytochemistry-1 (PG-504)
Chemistry, spectrum, potency, toxicity and pharmacokinetics:
• Aminoglycosides are basic, freely water soluble.
• They are not absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
• When given orally, their action is primarily confined to the gastrointestinal
tract
• They are excreted in active form in fairly large amounts in the urine.
• They are more commonly given intramuscularly or by perfusion.
• They act directly on the bacterial ribosome, where they inhibit protein
synthesis.
Side effects
• The undesirable side effects particularly nephrotoxicity, have lid to
restrictions in their systemic use.
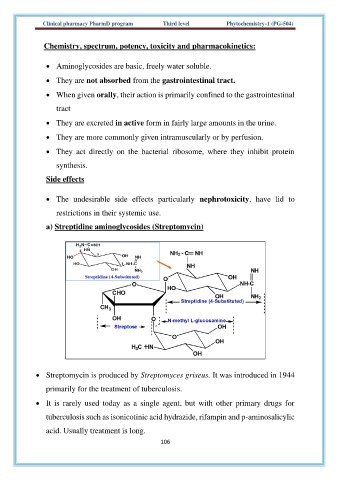
a) Streptidine aminoglycosides (Streptomycin)
• Streptomycin is produced by Streptomyces griseus. It was introduced in 1944
primarily for the treatment of tuberculosis.
• It is rarely used today as a single agent, but with other primary drugs for
tuberculosis such as isonicotinic acid hydrazide, rifampin and p-aminosalicylic
acid. Usually treatment is long.
106