Page 223 - Operations Strategy
P. 223
198 CHAPTER 6 • PRoCEss TECHnology sTRATEgy
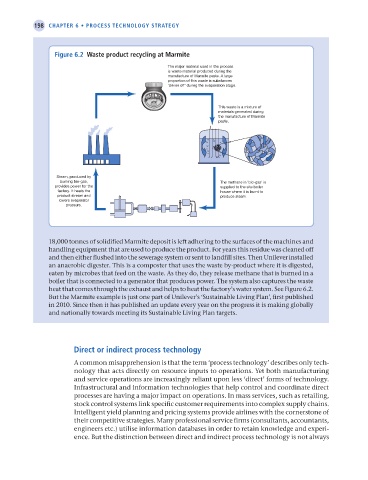
Figure 6.2 Waste product recycling at Marmite
The major material used in the process
is waste material produced during the
manufacture of Marmite paste. A large
proportion of this waste is substances
'driven o ' during the evaporation stage.
This waste is a mixture of
materials generated during
the manufacture of Marmite
paste.
Steam, produced by
burning bio-gas, The methane in 'bio-gas' is
provides power for the supplied to the site boiler
factory. It heats the house where it is burnt to
product stream and produce steam.
lowers evaporator
pressure.
18,000 tonnes of solidified Marmite deposit is left adhering to the surfaces of the machines and
handling equipment that are used to produce the product. For years this residue was cleaned off
and then either flushed into the sewerage system or sent to landfill sites. Then Unilever installed
an anaerobic digester. This is a composter that uses the waste by-product where it is digested,
eaten by microbes that feed on the waste. As they do, they release methane that is burned in a
boiler that is connected to a generator that produces power. The system also captures the waste
heat that comes through the exhaust and helps to heat the factory’s water system. See Figure 6.2.
But the Marmite example is just one part of Unilever’s ‘Sustainable Living Plan’, first published
in 2010. Since then it has published an update every year on the progress it is making globally
and nationally towards meeting its Sustainable Living Plan targets.
Direct or indirect process technology
A common misapprehension is that the term ‘process technology’ describes only tech-
nology that acts directly on resource inputs to operations. Yet both manufacturing
and service operations are increasingly reliant upon less ‘direct’ forms of technology.
Infrastructural and information technologies that help control and coordinate direct
processes are having a major impact on operations. In mass services, such as retailing,
stock control systems link specific customer requirements into complex supply chains.
Intelligent yield planning and pricing systems provide airlines with the cornerstone of
their competitive strategies. Many professional service firms (consultants, accountants,
engineers etc.) utilise information databases in order to retain knowledge and experi-
ence. But the distinction between direct and indirect process technology is not always
M06 Operations Strategy 62492.indd 198 02/03/2017 13:05