Page 270 - Operations Strategy
P. 270
sETTIng THE dIRECTIon 245
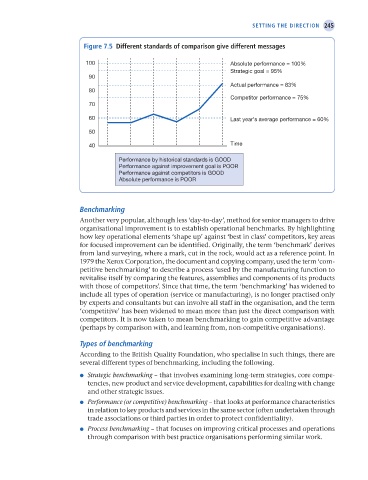
Figure 7.5 Different standards of comparison give different messages
100 Absolute performance = 100%
Strategic goal = 95%
90
Actual performance = 83%
80
Competitor performance = 75%
70
60 Last year’s average performance = 60%
50
40 Time
Performance by historical standards is GOOD
Performance against improvement goal is POOR
Performance against competitors is GOOD
Absolute performance is POOR
Benchmarking
Another very popular, although less ‘day-to-day’, method for senior managers to drive
organisational improvement is to establish operational benchmarks. By highlighting
how key operational elements ‘shape up’ against ‘best in class’ competitors, key areas
for focused improvement can be identified. Originally, the term ‘benchmark’ derives
from land surveying, where a mark, cut in the rock, would act as a reference point. In
1979 the Xerox Corporation, the document and copying company, used the term ‘com-
petitive benchmarking’ to describe a process ‘used by the manufacturing function to
revitalise itself by comparing the features, assemblies and components of its products
with those of competitors’. Since that time, the term ‘benchmarking’ has widened to
include all types of operation (service or manufacturing), is no longer practised only
by experts and consultants but can involve all staff in the organisation, and the term
‘competitive’ has been widened to mean more than just the direct comparison with
competitors. It is now taken to mean benchmarking to gain competitive advantage
(perhaps by comparison with, and learning from, non-competitive organisations).
Types of benchmarking
According to the British Quality Foundation, who specialise in such things, there are
several different types of benchmarking, including the following.
● Strategic benchmarking – that involves examining long-term strategies, core compe-
tencies, new product and service development, capabilities for dealing with change
and other strategic issues.
● Performance (or competitive) benchmarking – that looks at performance characteristics
in relation to key products and services in the same sector (often undertaken through
trade associations or third parties in order to protect confidentiality).
● Process benchmarking – that focuses on improving critical processes and operations
through comparison with best practice organisations performing similar work.
M07 Operations Strategy 62492.indd 245 02/03/2017 13:06