Page 344 - Operations Strategy
P. 344
mAinTAining AlignmEnT ovER TimE 319
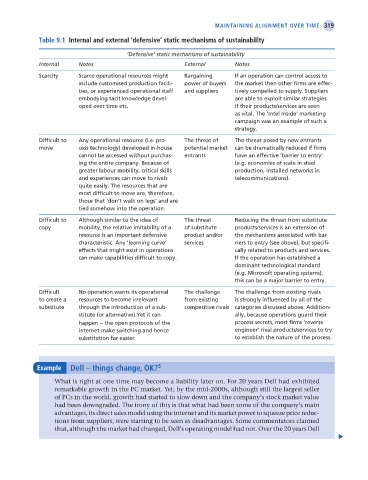
Table 9.1 internal and external ‘defensive’ static mechanisms of sustainability
‘Defensive’ static mechanisms of sustainability
Internal Notes External Notes
Scarcity Scarce operational resources might Bargaining If an operation can control access to
include customised production facili- power of buyers the market then other firms are effec-
ties, or experienced operational staff and suppliers tively compelled to supply. Suppliers
embodying tacit knowledge devel- are able to exploit similar strategies
oped over time etc. if their products/services are seen
as vital. The ‘Intel Inside’ marketing
campaign was an example of such a
strategy.
Difficult to Any operational resource (i.e. pro- The threat of The threat posed by new entrants
move cess technology) developed in-house potential market can be dramatically reduced if firms
cannot be accessed without purchas- entrants have an effective ‘barrier to entry’
ing the entire company. Because of (e.g. economies of scale in steel
greater labour mobility, critical skills production, installed networks in
and experiences can move to rivals telecommunications).
quite easily. The resources that are
most difficult to move are, therefore,
those that ‘don’t walk on legs’ and are
tied somehow into the operation.
Difficult to Although similar to the idea of The threat Reducing the threat from substitute
copy mobility, the relative imitability of a of substitute products/services is an extension of
resource is an important defensive product and/or the mechanisms associated with bar-
characteristic. Any ‘learning curve’ services riers to entry (see above), but specifi-
effects that might exist in operations cally related to products and services.
can make capabilities difficult to copy. If the operation has established a
dominant technological standard
(e.g. Microsoft operating systems),
this can be a major barrier to entry.
Difficult No operation wants its operational The challenge The challenge from existing rivals
to create a resources to become irrelevant from existing is strongly influenced by all of the
substitute through the introduction of a sub- competitive rivals categories discussed above. Addition-
stitute (or alternative).Yet it can ally, because operations guard their
happen – the open protocols of the process secrets, most firms ‘reverse
internet make switching and hence engineer’ rival products/services to try
substitution far easier. to establish the nature of the process.
example dell – things change, oK? 5
What is right at one time may become a liability later on. For 20 years Dell had exhibited
remarkable growth in the PC market. Yet, by the mid-2000s, although still the largest seller
of PCs in the world, growth had started to slow down and the company’s stock market value
had been downgraded. The irony of this is that what had been some of the company’s main
advantages, its direct sales model using the internet and its market power to squeeze price reduc-
tions from suppliers, were starting to be seen as disadvantages. Some commentators claimed
that, although the market had changed, Dell’s operating model had not. Over the 20 years Dell
M09 Operations Strategy 62492.indd 319 02/03/2017 13:27