Page 346 - Operations Strategy
P. 346
WHAT AnAlysis is nEEdEd foR foRmulATion? 321
one of the first academics to advocate a resource-based view of the firm, argued that
conceptually we tend to treat organisational resources as an ‘amorphous heap’. In fact,
6
the widely applied strategy management tool SWOT analysis is a good starting point for
the analysis of operations resources. This mechanism explicitly links internal (strengths
and weaknesses) and external (opportunities and threats) factors. And although SWOT
analysis is extremely difficult to incorporate into an effective planning process, the
‘strengths and weaknesses’ part of SWOT is particularly useful. Table 9.2 lists some pos-
sible operations factors that might be included in such an analysis.
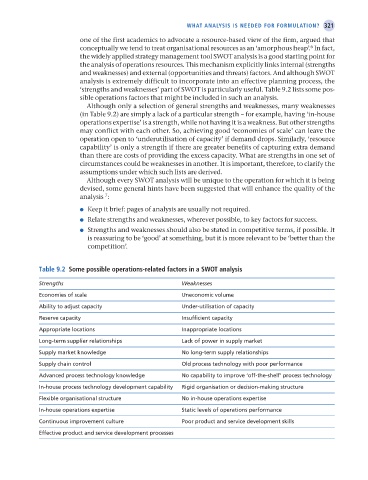
Although only a selection of general strengths and weaknesses, many weaknesses
(in Table 9.2) are simply a lack of a particular strength – for example, having ‘in-house
operations expertise’ is a strength, while not having it is a weakness. But other strengths
may conflict with each other. So, achieving good ‘economies of scale’ can leave the
operation open to ‘underutilisation of capacity’ if demand drops. Similarly, ‘resource
capability’ is only a strength if there are greater benefits of capturing extra demand
than there are costs of providing the excess capacity. What are strengths in one set of
circumstances could be weaknesses in another. It is important, therefore, to clarify the
assumptions under which such lists are derived.
Although every SWOT analysis will be unique to the operation for which it is being
devised, some general hints have been suggested that will enhance the quality of the
7
analysis :
● Keep it brief: pages of analysis are usually not required.
● Relate strengths and weaknesses, wherever possible, to key factors for success.
● Strengths and weaknesses should also be stated in competitive terms, if possible. It
is reassuring to be ‘good’ at something, but it is more relevant to be ‘better than the
competition’.
Table 9.2 some possible operations-related factors in a sWoT analysis
Strengths Weaknesses
Economies of scale Uneconomic volume
Ability to adjust capacity Under-utilisation of capacity
Reserve capacity Insufficient capacity
Appropriate locations Inappropriate locations
Long-term supplier relationships Lack of power in supply market
Supply market knowledge No long-term supply relationships
Supply chain control Old process technology with poor performance
Advanced process technology knowledge No capability to improve ‘off-the-shelf’ process technology
In-house process technology development capability Rigid organisation or decision-making structure
Flexible organisational structure No in-house operations expertise
In-house operations expertise Static levels of operations performance
Continuous improvement culture Poor product and service development skills
Effective product and service development processes
M09 Operations Strategy 62492.indd 321 02/03/2017 13:27