Page 110 - parasitology for medical and clinical laboratoryprofessionals
P. 110
90 CHAPTER 4
Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
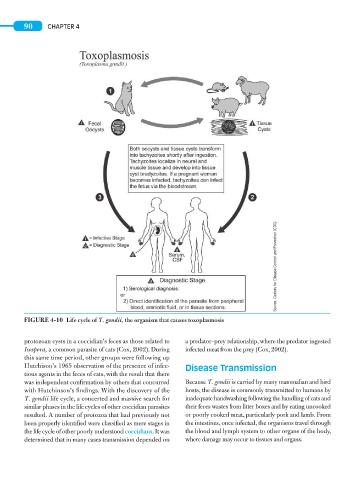
FIGURE 4-10 Life cycle of T. gondii, the organism that causes toxoplasmosis
protozoan cysts in a coccidian’s feces as those related to a predator–prey relationship, where the predator ingested
Isospora, a common parasite of cats (Cox, 2002). During infected meat from the prey (Cox, 2002).
this same time period, other groups were following up
Hutchison’s 1965 observation of the presence of infec- Disease Transmission
tious agents in the feces of cats, with the result that there
was independent confirmation by others that concurred Because T. gondii is carried by many mammalian and bird
with Hutchinson’s findings. With the discovery of the hosts, the disease is commonly transmitted to humans by
T. gondii life cycle, a concerted and massive search for inadequate handwashing following the handling of cats and
similar phases in the life cycles of other coccidian parasites their feces wastes from litter boxes and by eating uncooked
resulted. A number of protozoa that had previously not or poorly cooked meat, particularly pork and lamb. From
been properly identified were classified as mere stages in the intestines, once infected, the organisms travel through
the life cycle of other poorly understood coccidians. It was the blood and lymph system to other organs of the body,
determined that in many cases transmission depended on where damage may occur to tissues and organs.