Page 126 - parasitology for medical and clinical laboratoryprofessionals
P. 126
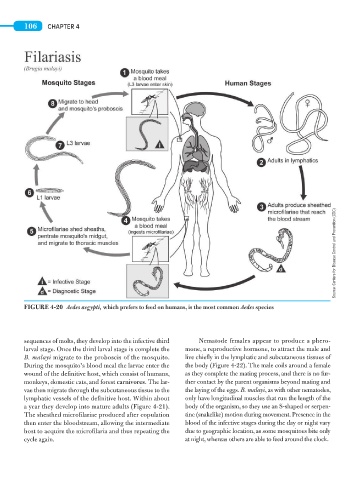
106 CHAPTER 4
Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
FIGURE 4-20 Aedes aegypti, which prefers to feed on humans, is the most common Aedes species
sequences of molts, they develop into the infective third Nematode females appear to produce a phero-
larval stage. Once the third larval stage is complete the mone, a reproductive hormone, to attract the male and
B. malayi migrate to the proboscis of the mosquito. live chiefly in the lymphatic and subcutaneous tissues of
During the mosquito’s blood meal the larvae enter the the body (Figure 4-22). The male coils around a female
wound of the definitive host, which consist of humans, as they complete the mating process, and there is no fur-
monkeys, domestic cats, and forest carnivores. The lar- ther contact by the parent organisms beyond mating and
vae then migrate through the subcutaneous tissue to the the laying of the eggs. B. malayi, as with other nematodes,
lymphatic vessels of the definitive host. Within about only have longitudinal muscles that run the length of the
a year they develop into mature adults (Figure 4-21). body of the organism, so they use an S-shaped or serpen-
The sheathed microfilariae produced after copulation tine (snakelike) motion during movement. Presence in the
then enter the bloodstream, allowing the intermediate blood of the infective stages during the day or night vary
host to acquire the microfilaria and thus repeating the due to geographic location, as some mosquitoes bite only
cycle again. at night, whereas others are able to feed around the clock.