Page 127 - parasitology for medical and clinical laboratoryprofessionals
P. 127
Blood (Intracellular) and Other Tissue Protozoa 107
Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
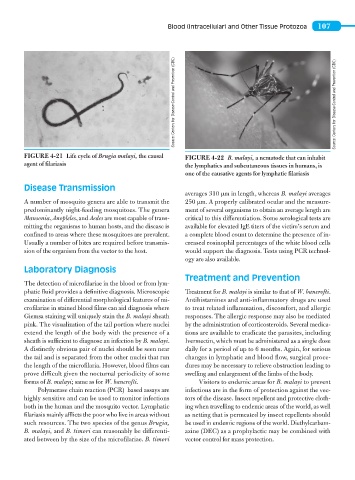
FIGURE 4-21 Life cycle of Brugia malayi, the causal FIGURE 4-22 B. malayi, a nematode that can inhabit
agent of filariasis the lymphatics and subcutaneous tissues in humans, is
one of the causative agents for lymphatic filariasis
Disease Transmission
averages 310 μm in length, whereas B. malayi averages
A number of mosquito genera are able to transmit the 250 μm. A properly calibrated ocular and the measure-
predominantly night-feeding mosquitoes. The genera ment of several organisms to obtain an average length are
Mansonia, Anopleles, and Aedes are most capable of trans- critical to this differentiation. Some serological tests are
mitting the organisms to human hosts, and the disease is available for elevated IgE titers of the victim’s serum and
confined to areas where these mosquitoes are prevalent. a complete blood count to determine the presence of in-
Usually a number of bites are required before transmis- creased eosinophil percentages of the white blood cells
sion of the organism from the vector to the host. would support the diagnosis. Tests using PCR technol-
ogy are also available.
Laboratory Diagnosis
Treatment and Prevention
The detection of microfilariae in the blood or from lym-
phatic fluid provides a definitive diagnosis. Microscopic Treatment for B. malayi is similar to that of W. bancrofti.
examination of differential morphological features of mi- Antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs are used
crofilariae in stained blood films can aid diagnosis where to treat related inflammation, discomfort, and allergic
Giemsa staining will uniquely stain the B. malayi sheath responses. The allergic response may also be mediated
pink. The visualization of the tail portion where nuclei by the administration of corticosteroids. Several medica-
extend the length of the body with the presence of a tions are available to eradicate the parasites, including
sheath is sufficient to diagnose an infection by B. malayi. Ivermectin, which must be administered as a single dose
A distinctly obvious pair of nuclei should be seen near daily for a period of up to 6 months. Again, for serious
the tail and is separated from the other nuclei that run changes in lymphatic and blood flow, surgical proce-
the length of the microfilaria. However, blood films can dures may be necessary to relieve obstruction leading to
prove difficult given the nocturnal periodicity of some swelling and enlargement of the limbs of the body.
forms of B. malayi; same as for W. bancrofti. Visitors to endemic areas for B. malayi to prevent
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)–based assays are infections are in the form of protection against the vec-
highly sensitive and can be used to monitor infections tors of the disease. Insect repellent and protective cloth-
both in the human and the mosquito vector. Lymphatic ing when travelling to endemic areas of the world, as well
filariasis mainly afflicts the poor who live in areas without as netting that is permeated by insect repellents should
such resources. The two species of the genus Brugia, be used in endemic regions of the world. Diethylcarbam-
B. malayi, and B. timori can reasonably be differenti- azine (DEC) as a prophylactic may be combined with
ated between by the size of the microfilariae. B. timori vector control for mass protection.