Page 48 - parasitology for medical and clinical laboratoryprofessionals
P. 48
28 CHAPTER 2
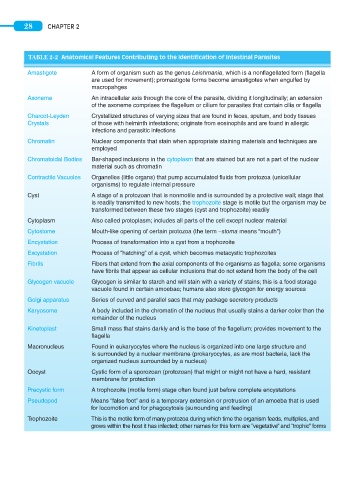
TABLE 2-2 Anatomical Features Contributing to the Identification of Intestinal Parasites
Amastigote A form of organism such as the genus Leishmania, which is a nonflagellated form (flagella
are used for movement); promastigote forms become amastigotes when engulfed by
macropahges
Axoneme An intracellular axis through the core of the parasite, dividing it longitudinally; an extension
of the axoneme comprises the flagellum or cilium for parasites that contain cilia or flagella
Charcot-Leyden Crystallized structures of varying sizes that are found in feces, sputum, and body tissues
Crystals of those with helminth infestations; originate from eosinophils and are found in allergic
infections and parasitic infections
Chromatin Nuclear components that stain when appropriate staining materials and techniques are
employed
Chromatoidal Bodies Bar-shaped inclusions in the cytoplasm that are stained but are not a part of the nuclear
material such as chromatin
Contractile Vacuoles Organelles (little organs) that pump accumulated fluids from protozoa (unicellular
organisms) to regulate internal pressure
Cyst A stage of a protozoan that is nonmotile and is surrounded by a protective wall; stage that
is readily transmitted to new hosts; the trophozoite stage is motile but the organism may be
transformed between these two stages (cyst and trophozoite) readily
Cytoplasm Also called protoplasm; includes all parts of the cell except nuclear material
Cytostome Mouth-like opening of certain protozoa (the term –stoma means “mouth”)
Encystation Process of transformation into a cyst from a trophozoite
Excystation Process of “hatching” of a cyst, which becomes metacystic trophozoites
Fibrils Fibers that extend from the axial components of the organisms as flagella; some organisms
have fibrils that appear as cellular inclusions that do not extend from the body of the cell
Glycogen vacuole Glycogen is similar to starch and will stain with a variety of stains; this is a food storage
vacuole found in certain amoebae; humans also store glycogen for energy sources
Golgi apparatus Series of curved and parallel sacs that may package secretory products
Karyosome A body included in the chromatin of the nucleus that usually stains a darker color than the
remainder of the nucleus
Kinetoplast Small mass that stains darkly and is the base of the flagellum; provides movement to the
flagella
Macronucleus Found in eukaryocytes where the nucleus is organized into one large structure and
is surrounded by a nuclear membrane (prokaryocytes, as are most bacteria, lack the
organized nucleus surrounded by a nucleus)
Oocyst Cystic form of a sporozoan (protozoan) that might or might not have a hard, resistant
membrane for protection
Precystic form A trophozoite (motile form) stage often found just before complete encystations
Pseudopod Means “false foot” and is a temporary extension or protrusion of an amoeba that is used
for locomotion and for phagocytosis (surrounding and feeding)
Trophozoite This is the motile form of many protozoa during which time the organism feeds, multiplies, and
grows within the host it has infected; other names for this form are “vegetative” and “trophic” forms