Page 20 - Ilmu Tanah
P. 20
The Chemistry and Fertility of Soils under Tropical Weeds 7
50
CEC (cmol c kg -1 ) 30
40
20
10
0
4 5 6 7
pH
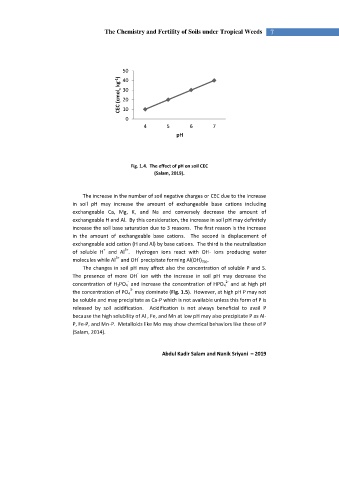
Fig. 1.4. The effect of pH on soil CEC
(Salam, 2019).
The increase in the number of soil negative charges or CEC due to the increase
in soil pH may increase the amount of exchangeable base cations including
exchangeable Ca, Mg, K, and Na and conversely decrease the amount of
exchangeable H and Al. By this consideration, the increase in soil pH may definitely
increase the soil base saturation due to 3 reasons. The first reason is the increase
in the amount of exchangeable base cations. The second is displacement of
exchangeable acid cation (H and Al) by base cations. The third is the neutralization
+ 3+
of soluble H and Al . Hydrogen ions react with OH- ions producing water
3+ -
molecules while Al and OH precipitate forming Al(OH) 3(s) .
The changes in soil pH may affect also the concentration of soluble P and S.
-
The presence of more OH ion with the increase in soil pH may decrease the
- 2-
concentration of H 2 PO 4 and increase the concentration of HPO 4 and at high pH
3-
the concentration of PO 4 may dominate (Fig. 1.5). However, at high pH P may not
be soluble and may precipitate as Ca-P which is not available unless this form of P is
released by soil acidification. Acidification is not always beneficial to avail P
because the high solubility of Al , Fe, and Mn at low pH may also precipitate P as Al-
P, Fe-P, and Mn-P. Metalloids like Mo may show chemical behaviors like those of P
(Salam, 2014).
Abdul Kadir Salam and Nanik Sriyani – 2019