Page 20 - CJO_F17_GLAUCOMA_SUPPLEMENT
P. 20
C CLINICAL RESEARCH
POSTERIOR POLE ASSESSMENT
Optic Nerve and RNFL Evaluation
The contemporary definition of glaucoma hinges on structural change of the optic nerve complex. 148-150 Structural
damage is often the presenting sign of glaucoma, and progression of that damage is highly predictive of future
functional loss, typically preceding detection of that loss by months to years. 151,152 It warrants emphasizing that up
to 40% of an individual’s retinal ganglion cells can be lost before a visual field defect is detectable through standard
automated perimetry. The OHTS highlighted this fact, as two-thirds of the observation cohort who converted to
51
glaucoma did so based on optic nerve head (ONH) appearance alone. For these reasons, careful and systematic
153
stereoscopic evaluation of the ONH and retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL), complemented by routine photography
and ancillary structural and functional assessment when clinically indicated, remains essential in the diagnosis and
management of glaucoma.
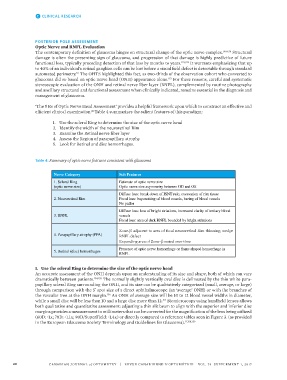
‘The 5 Rs of Optic Nerve Head Assessment’ provides a helpful framework upon which to construct an effective and
efficient clinical examination. Table 4 summarizes the salient features of this paradigm:
41
1. Use the scleral Ring to determine the size of the optic nerve head
2. Identify the width of the neuroretinal Rim
3. Examine the Retinal nerve fiber layer
4. Assess the Region of parapapillary atrophy
5. Look for Retinal and disc hemorrhages.
Table 4: Summary of optic nerve features consistent with glaucoma
Nerve Category Sub Features
1. Scleral Ring Estimate of optic nerve size
(optic nerve size) Optic nerve size asymmetry between OD and OS
Diffuse loss: break down of ISNT rule, excavation of rim tissue
2. Neuroretinal Rim Focal loss: bayonetting of blood vessels, baring of blood vessels
No pallor
Diffuse loss: loss of bright striations, increased clarity of tertiary blood
3. RNFL vessels
Focal loss: area of dark RNFL bounded by bright striations
Zone-β adjacent to area of focal neuroretinal Rim thinning, wedge
4. Parapapillary atrophy (PPA) RNFL defect
Expanding area of Zone-β noted over time
Presence of optic nerve hemorrhage or flame shaped hemorrhage in
5. Retinal (disc) hemorrhages
RNFL
1. Use the scleral Ring to determine the size of the optic nerve head
An accurate assessment of the ONH depends upon an understanding of its size and shape, both of which can vary
dramatically between patients. 154,155 The normally slightly vertically oval disc is delineated by the thin white para-
papillary scleral Ring surrounding the ONH, and its size can be qualitatively categorized (small, average, or large)
through comparison with the 5 spot size of a direct ophthalmoscope (an ‘average’ ONH) or with the branches of
°
the vascular tree at the ONH margin. An ONH of average size will be 10 to 12 blood vessel widths in diameter,
156
while a small disc will be less than 10 and a large disc more than 12. Biomicroscopy using handheld lenses allows
157
both qualitative and quantitative assessment: adjusting a thin slit beam to align with the superior and inferior disc
margins provides a measurement in millimeters that can be corrected for the magnification of the lens being utilized
(60D: ~1x; 78D: ~1.1x; 90D/SuperField: ~1.4x) or directly compared to reference tables seen in Figure 3. (as provided
in the European Glaucoma Society Terminology and Guidelines for Glaucoma). 11,158,159
20 CANADIAN JOURNAL of OPTOMETRY | REVUE CANADIENNE D’OPTOMÉTRIE VOL. 79 SUPPLEMENT 1, 2017