Page 254 - Basic Electrical Engineering
P. 254
35. Derive the formula used in calculating the temperature coefficient of resistance at any
temperature from its given value at any particular temperature.
B. Numerical Problems
36. A long copper wire has a resistance of 25 Ω at 40°C. Its resistance becomes 45 Ω when the
temperature is 100°C. Calculate the value of its resistance at 0°C.
[Ans 11.7 Ω]
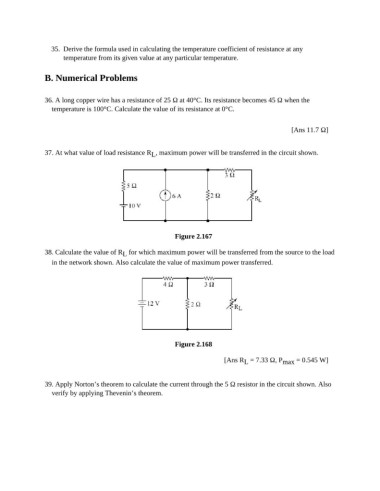
37. At what value of load resistance R , maximum power will be transferred in the circuit shown.
L
Figure 2.167
38. Calculate the value of R for which maximum power will be transferred from the source to the load
L
in the network shown. Also calculate the value of maximum power transferred.
Figure 2.168
[Ans R = 7.33 Ω, P max = 0.545 W]
L
39. Apply Norton’s theorem to calculate the current through the 5 Ω resistor in the circuit shown. Also
verify by applying Thevenin’s theorem.