Page 562 - Basic Electrical Engineering
P. 562
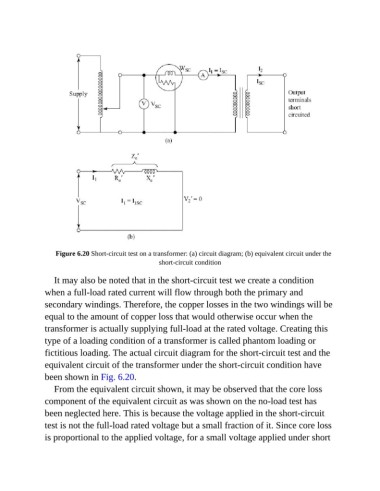
Figure 6.20 Short-circuit test on a transformer: (a) circuit diagram; (b) equivalent circuit under the
short-circuit condition
It may also be noted that in the short-circuit test we create a condition
when a full-load rated current will flow through both the primary and
secondary windings. Therefore, the copper losses in the two windings will be
equal to the amount of copper loss that would otherwise occur when the
transformer is actually supplying full-load at the rated voltage. Creating this
type of a loading condition of a transformer is called phantom loading or
fictitious loading. The actual circuit diagram for the short-circuit test and the
equivalent circuit of the transformer under the short-circuit condition have
been shown in Fig. 6.20.
From the equivalent circuit shown, it may be observed that the core loss
component of the equivalent circuit as was shown on the no-load test has
been neglected here. This is because the voltage applied in the short-circuit
test is not the full-load rated voltage but a small fraction of it. Since core loss
is proportional to the applied voltage, for a small voltage applied under short