Page 448 - Fiber Optic Communications Fund
P. 448
Nonlinear Effects in Fibers 429
0.1
0.08
0.06 Blue shift Red shift
Electrical field (arb. units) –0.02 0
0.04
0.02
–0.04
–0.06
–0.08
–0.1
–1500 –1000 –500 0 500 1000 1500
Time, T (ps)
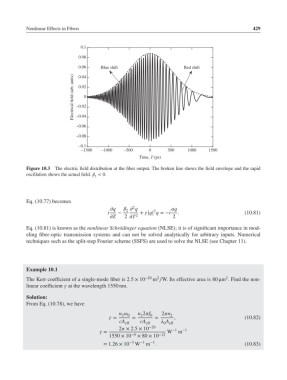
Figure 10.3 The electric field distribution at the fiber output. The broken line shows the field envelope and the rapid
oscillation shows the actual field. < 0.
2
Eq. (10.77) becomes
2
q q 2 q
2
i − + |q| q =−i . (10.81)
Z 2 T 2 2
Eq. (10.81) is known as the nonlinear Schrödinger equation (NLSE); it is of significant importance in mod-
eling fiber-optic transmission systems and can not be solved analytically for arbitrary inputs. Numerical
techniques such as the split-step Fourier scheme (SSFS) are used to solve the NLSE (see Chapter 11).
Example 10.1
2
2
The Kerr coefficient of a single-mode fiber is 2.5 × 10 −20 m ∕W. Itseffectiveareais80 μm . Find the non-
linear coefficient at the wavelength 1550 nm.
Solution:
From Eq. (10.78), we have
n 0 n 2f 0 2n 2
2
2
= = = , (10.82)
cA eff cA eff A
0 eff
2 × 2.5 × 10 −20 −1 −1
= W m
1550 × 10 −9 × 80 × 10 −12
−1
= 1.26 × 10 −3 W −1 m . (10.83)