Page 347 - Introduction to Business
P. 347
CHAPTER 9 Developing the Product and Pricing Mixes 321
In making this calculation, it is helpful to understand that because the price EXHIBIT 9.2
exceeds the cost per unit by $6, every time a unit is sold, the development cost plus
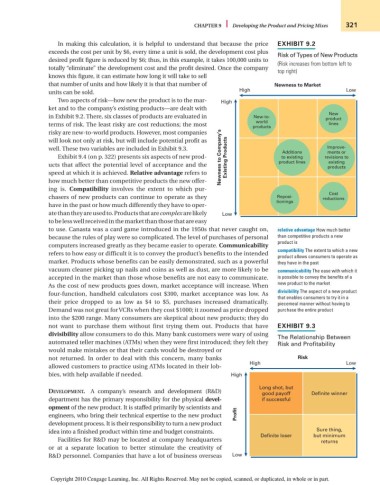
Risk of Types of New Products
desired profit figure is reduced by $6; thus, in this example, it takes 100,000 units to
(Risk increases from bottom left to
totally “eliminate” the development cost and the profit desired. Once the company
top right)
knows this figure, it can estimate how long it will take to sell
that number of units and how likely it is that that number of Newness to Market
units can be sold. High Low
Two aspects of risk—how new the product is to the mar- High
ket and to the company’s existing products—are dealt with
New
in Exhibit 9.2. There, six classes of products are evaluated in New-to- product
world
terms of risk. The least risky are cost reductions; the most products lines
risky are new-to-world products. However, most companies
will look not only at risk, but will include potential profit as
well. These two variables are included in Exhibit 9.3. Additions Improve-
ments or
Exhibit 9.4 (on p. 322) presents six aspects of new prod- Newness to Company’s Existing Products to existing revisions to
existing
ucts that affect the potential level of acceptance and the product lines products
speed at which it is achieved. Relative advantage refers to
how much better than competitive products the new offer-
ing is. Compatibility involves the extent to which pur-
Cost
chasers of new products can continue to operate as they Reposi- reductions
tionings
have in the past or how much differently they have to oper-
atethantheyareusedto.Productsthatarecomplexarelikely Low
tobelesswellreceivedinthemarketthanthosethatareeasy
to use. Canasta was a card game introduced in the 1950s that never caught on, relative advantage How much better
because the rules of play were so complicated. The level of purchases of personal than competitive products a new
product is
computers increased greatly as they became easier to operate. Communicability
compatibility The extent to which a new
refers to how easy or difficult it is to convey the product’s benefits to the intended
product allows consumers to operate as
market. Products whose benefits can be easily demonstrated, such as a powerful they have in the past
vacuum cleaner picking up nails and coins as well as dust, are more likely to be communicability The ease with which it
accepted in the market than those whose benefits are not easy to communicate. is possible to convey the benefits of a
As the cost of new products goes down, market acceptance will increase. When new product to the market
four-function, handheld calculators cost $300, market acceptance was low. As divisibility The aspect of a new product
that enables consumers to try it in a
their price dropped to as low as $4 to $5, purchases increased dramatically. piecemeal manner without having to
Demand was not great for VCRs when they cost $1000; it zoomed as price dropped purchase the entire product
into the $200 range. Many consumers are skeptical about new products; they do
not want to purchase them without first trying them out. Products that have EXHIBIT 9.3
divisibility allow consumers to do this. Many bank customers were wary of using
The Relationship Between
automated teller machines (ATMs) when they were first introduced; they felt they Risk and Profitability
would make mistakes or that their cards would be destroyed or
not returned. In order to deal with this concern, many banks Risk
High Low
allowed customers to practice using ATMs located in their lob-
bies, with help available if needed. High
Long shot, but
DEVELOPMENT. A company’s research and development (R&D) good payoff Definite winner
department has the primary responsibility for the physical devel- if successful
opment of the new product. It is staffed primarily by scientists and
engineers, who bring their technical expertise to the new product Profit
development process. It is their responsibility to turn a new product
idea into a finished product within time and budget constraints. Sure thing,
Definite loser but minimum
Facilities for R&D may be located at company headquarters returns
or at a separate location to better stimulate the creativity of
R&D personnel. Companies that have a lot of business overseas Low
Copyright 2010 Cengage Learning, Inc. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part.