Page 59 - Introduction to Business
P. 59
CHAPTER 1 What Is Business? 33
Purchasing Power Parity
As you can infer from the preceding discussion, annual GNI per capita is an impor-
tant measure of how well consumers of a country are doing in that particular year.
It is determined by dividing a country’s nominal GNI by the country’s population
for that year.
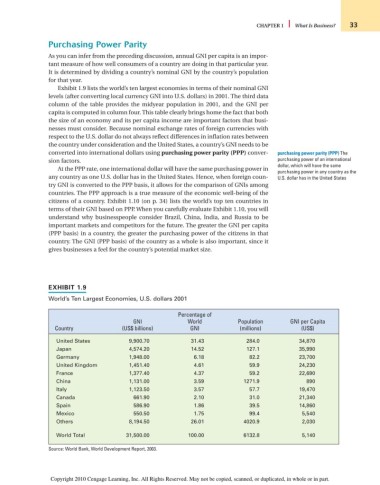
Exhibit 1.9 lists the world’s ten largest economies in terms of their nominal GNI
levels (after converting local currency GNI into U.S. dollars) in 2001. The third data
column of the table provides the midyear population in 2001, and the GNI per
capita is computed in column four. This table clearly brings home the fact that both
the size of an economy and its per capita income are important factors that busi-
nesses must consider. Because nominal exchange rates of foreign currencies with
respect to the U.S. dollar do not always reflect differences in inflation rates between
the country under consideration and the United States, a country’s GNI needs to be
converted into international dollars using purchasing power parity (PPP) conver- purchasing power parity (PPP) The
sion factors. purchasing power of an international
dollar, which will have the same
At the PPP rate, one international dollar will have the same purchasing power in
purchasing power in any country as the
any country as one U.S. dollar has in the United States. Hence, when foreign coun- U.S. dollar has in the United States
try GNI is converted to the PPP basis, it allows for the comparison of GNIs among
countries. The PPP approach is a true measure of the economic well-being of the
citizens of a country. Exhibit 1.10 (on p. 34) lists the world’s top ten countries in
terms of their GNI based on PPP. When you carefully evaluate Exhibit 1.10, you will
understand why businesspeople consider Brazil, China, India, and Russia to be
important markets and competitors for the future. The greater the GNI per capita
(PPP basis) in a country, the greater the purchasing power of the citizens in that
country. The GNI (PPP basis) of the country as a whole is also important, since it
gives businesses a feel for the country’s potential market size.
EXHIBIT 1.9
World’s Ten Largest Economies, U.S. dollars 2001
Percentage of
GNI World Population GNI per Capita
Country (US$ billions) GNI (millions) (US$)
United States 9,900.70 31.43 284.0 34,870
Japan 4,574.20 14.52 127.1 35,990
Germany 1,948.00 6.18 82.2 23,700
United Kingdom 1,451.40 4.61 59.9 24,230
France 1,377.40 4.37 59.2 22,690
China 1,131.00 3.59 1271.9 890
Italy 1,123.50 3.57 57.7 19,470
Canada 661.90 2.10 31.0 21,340
Spain 586.90 1.86 39.5 14,860
Mexico 550.50 1.75 99.4 5,540
Others 8,194.50 26.01 4020.9 2,030
World Total 31,500.00 100.00 6132.8 5,140
Source: World Bank, World Development Report, 2003.
Copyright 2010 Cengage Learning, Inc. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part.