Page 60 - Introduction to Business
P. 60
34 PART 1 The Nature of Contemporary Business
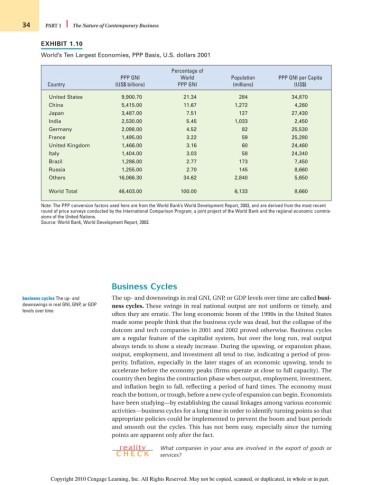
EXHIBIT 1.10
World’s Ten Largest Economies, PPP Basis, U.S. dollars 2001
Percentage of
PPP GNI World Population PPP GNI per Capita
Country (US$ billions) PPP GNI (millions) (US$)
United States 9,900.70 21.34 284 34,870
China 5,415.00 11.67 1,272 4,260
Japan 3,487.00 7.51 127 27,430
India 2,530.00 5.45 1,033 2,450
Germany 2,098.00 4.52 82 25,530
France 1,495.00 3.22 59 25,280
United Kingdom 1,466.00 3.16 60 24,460
Italy 1,404.00 3.03 58 24,340
Brazil 1,286.00 2.77 173 7,450
Russia 1,255.00 2.70 145 8,660
Others 16,066.30 34.62 2,840 5,650
World Total 46,403.00 100.00 6,133 8,660
Note: The PPP conversion factors used here are from the World Bank’s World Development Report, 2003, and are derived from the most recent
round of price surveys conducted by the International Comparison Program, a joint project of the World Bank and the regional economic commis-
sions of the United Nations.
Source: World Bank, World Development Report, 2003.
Business Cycles
business cycles The up- and The up- and downswings in real GNI, GNP, or GDP levels over time are called busi-
downswings in real GNI, GNP, or GDP ness cycles. These swings in real national output are not uniform or timely, and
levels over time
often they are erratic. The long economic boom of the 1990s in the United States
made some people think that the business cycle was dead, but the collapse of the
dotcom and tech companies in 2001 and 2002 proved otherwise. Business cycles
are a regular feature of the capitalist system, but over the long run, real output
always tends to show a steady increase. During the upswing, or expansion phase,
output, employment, and investment all tend to rise, indicating a period of pros-
perity. Inflation, especially in the later stages of an economic upswing, tends to
accelerate before the economy peaks (firms operate at close to full capacity). The
country then begins the contraction phase when output, employment, investment,
and inflation begin to fall, reflecting a period of hard times. The economy must
reach the bottom, or trough, before a new cycle of expansion can begin. Economists
have been studying—by establishing the causal linkages among various economic
activities—business cycles for a long time in order to identify turning points so that
appropriate policies could be implemented to prevent the boom and bust periods
and smooth out the cycles. This has not been easy, especially since the turning
points are apparent only after the fact.
reality What companies in your area are involved in the export of goods or
CH ECK services?
Copyright 2010 Cengage Learning, Inc. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part.