Page 187 - BA2 Integrated Workbook - Student 2017
P. 187
Risk 2: probability
Example:
ABC is a furniture retailer. It offers a customer loan facility. If a new customer
requests a loan then ABC either refuses it, gives a high loan limit, or gives a low loan
limit. From a number of years past experience the probability that a new customer
makes a full repayment of a loan is known to be 0.95, whilst the probability of non-
repayment is 0.05 (these probabilities being independent of the size of loan limit).
The average profit on the loans, per customer is given by the following table.
Loan limit – High Loan limit – low
Full repayment $50 $20
Non-repayment ($200) ($30)
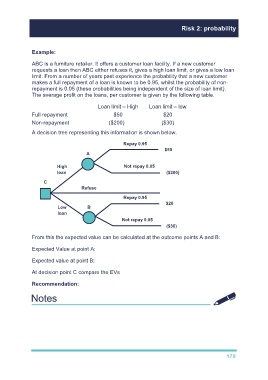
A decision tree representing this information is shown below.
Repay 0.95
$50
A
High Not repay 0.05
loan ($200)
C
Refuse
Repay 0.95
$20
Low B
loan
Not repay 0.05
($30)
From this the expected value can be calculated at the outcome points A and B:
Expected Value at point A: (0.95 × 50) + (0.05 × (200)) = 37.5
Expected value at point B: (0.95 × 20) + (0.05 × (30)) = 17.5
At decision point C compare the EVs of $37.5 and $17.5.
Recommendation: if a customer requests a loan give him/her a high loan limit.
Try TYU 8
179