Page 25 - FINAL CFA II SLIDES JUNE 2019 DAY 4
P. 25
LOS 13.a: Describe classifications of regulations and regulators. READING 11: CURRENCY EXCHANGE RATES: UNDERSTANDING EQUILIBRIUM VALUE
MODULE 13.1: ECONOMICS OF REGULATION
Regulations can be classified as:
• statutes (laws made by legislative bodies),
• administrative regulations (rules issued by government agencies or other bodies authorized by the government), or
• judicial law (findings of the court).
LOS 13.b: Describe uses of self-regulation in financial markets.
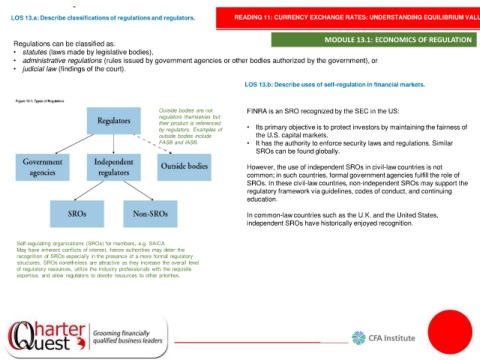
Outside bodies are not FINRA is an SRO recognized by the SEC in the US:
regulators themselves but
their product is referenced • Its primary objective is to protect investors by maintaining the fairness of
by regulators. Examples of
outside bodies include the U.S. capital markets.
FASB and IASB. • It has the authority to enforce security laws and regulations. Similar
SROs can be found globally.
However, the use of independent SROs in civil-law countries is not
common; in such countries, formal government agencies fulfill the role of
SROs. In these civil-law countries, non-independent SROs may support the
regulatory framework via guidelines, codes of conduct, and continuing
education.
In common-law countries such as the U.K. and the United States,
independent SROs have historically enjoyed recognition.
Self-regulating organizations (SROs) for members, e.g. SAICA
May have inherent conflicts of interest, hence authorities may deter the
recognition of SROs especially in the presence of a more formal regulatory
structures. SROs nonetheless are attractive as they increase the overall level
of regulatory resources, utilize the industry professionals with the requisite
expertise, and allow regulators to devote resources to other priorities.