Page 14 - FINAL CFA II SLIDES JUNE 2019 DAY 8
P. 14
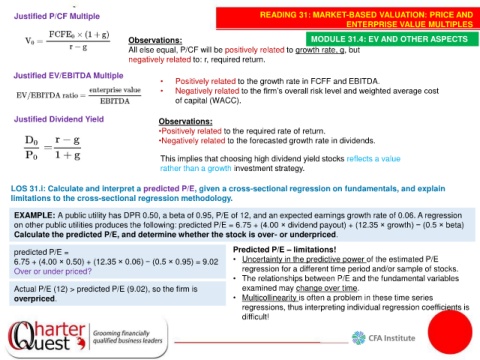
Justified P/CF Multiple READING 31: MARKET-BASED VALUATION: PRICE AND
ENTERPRISE VALUE MULTIPLES
Observations: MODULE 31.4: EV AND OTHER ASPECTS
All else equal, P/CF will be positively related to growth rate, g, but
negatively related to: r, required return.
Justified EV/EBITDA Multiple
• Positively related to the growth rate in FCFF and EBITDA.
• Negatively related to the firm’s overall risk level and weighted average cost
of capital (WACC).
Justified Dividend Yield Observations:
•Positively related to the required rate of return.
•Negatively related to the forecasted growth rate in dividends.
This implies that choosing high dividend yield stocks reflects a value
rather than a growth investment strategy.
LOS 31.i: Calculate and interpret a predicted P/E, given a cross-sectional regression on fundamentals, and explain
limitations to the cross-sectional regression methodology.
EXAMPLE: A public utility has DPR 0.50, a beta of 0.95, P/E of 12, and an expected earnings growth rate of 0.06. A regression
on other public utilities produces the following: predicted P/E = 6.75 + (4.00 × dividend payout) + (12.35 × growth) − (0.5 × beta)
Calculate the predicted P/E, and determine whether the stock is over- or underpriced.
predicted P/E = Predicted P/E – limitations!
6.75 + (4.00 × 0.50) + (12.35 × 0.06) − (0.5 × 0.95) = 9.02 • Uncertainty in the predictive power of the estimated P/E
Over or under priced? regression for a different time period and/or sample of stocks.
• The relationships between P/E and the fundamental variables
Actual P/E (12) > predicted P/E (9.02), so the firm is examined may change over time.
overpriced. • Multicollinearity is often a problem in these time series
regressions, thus interpreting individual regression coefficients is
difficult!