Page 9 - FINAL CFA II SLIDES JUNE 2019 DAY 8
P. 9
LOS 31.b: Calculate and interpret a justified price multiple. READING 31: MARKET-BASED VALUATION: PRICE AND
LOS 31.c: Describe rationales for and possible drawbacks ENTERPRISE VALUE MULTIPLES
to using alternative price multiples and dividend yield in
valuation. MODULE 31.4: EV AND OTHER ASPECTS
LOS 31.d: Calculate and interpret alternative price
multiples and dividend yield.
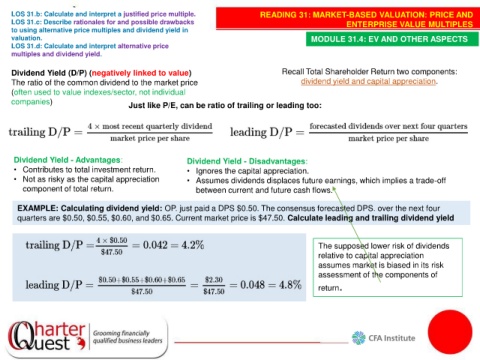
Dividend Yield (D/P) (negatively linked to value) Recall Total Shareholder Return two components:
The ratio of the common dividend to the market price dividend yield and capital appreciation.
(often used to value indexes/sector, not individual
companies)
Just like P/E, can be ratio of trailing or leading too:
Dividend Yield - Advantages: Dividend Yield - Disadvantages:
• Contributes to total investment return. • Ignores the capital appreciation.
• Not as risky as the capital appreciation • Assumes dividends displaces future earnings, which implies a trade-off
component of total return. between current and future cash flows.
EXAMPLE: Calculating dividend yield: OP. just paid a DPS $0.50. The consensus forecasted DPS. over the next four
quarters are $0.50, $0.55, $0.60, and $0.65. Current market price is $47.50. Calculate leading and trailing dividend yield
The supposed lower risk of dividends
relative to capital appreciation
assumes market is biased in its risk
assessment of the components of
return.