Page 60 - NUMINO TG_4A
P. 60
03Ancient Numerals Unit
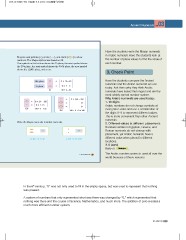
Mayans used pebbles ( ), sticks ( ), and shells ( ) to show Have the students write the Mayan numerals
numbers. The Mayan system was based on 20. in Arabic numerals.Have the students look at
The symbol on the bottom shows the 1’s place, the next symbol shows the number of place values to find the value of
the 20’s place, the next symbol shows the 360’s place, the next symbol each number.
shows the 7,200’s place, and so on.
3. Check Point
20’s place 2 20 = 40 Have the students compare the Ancient
1’s place 6 1=6
40 + 6 = 46 numerals and the Arabic numerals we use
46 1 360 = 360 today. Ask them why they think Arabic
0
0 numerals have lasted the longest and are the
360 360 + 0 + 0 = 360 most widely spread number system.
Why Arabic numerals are used today:
6 20 = 120 1. 10 digits
6 1=6
126 120 + 6 = 126 Arabic numbers do not change symbols at
every place value and use a combination of
the digits 0~9 to represent different values.
This is more convenient than other Ancient
Write the Mayan numerals in Arabic numerals. numerals.
2. Different values at different placements
Numbers written in Egyptian, Greece, and
67 121 Roman numerals do not change with
3 20 + 7 1 = 67 6 20 + 1 1 = 121
placement, yet Arabic numerals have a
different value when placed in different
locations.
3. 0 (zero)
Refer to .
3. Ancient Numerals 29 The Arabic number system is used all over the
world because of these reasons.
In the 6th century, “0” was not only used to fill in the empty space, but was used to represent that nothing
was present.
A system of numbers that only represented what was there was changed by “0,” which represented that
nothing was there and the course of Science, Mathematics, and much more. The addition of zero created a
much more efficient number system.
4A Unit 03 043
Mayans used pebbles ( ), sticks ( ), and shells ( ) to show Have the students write the Mayan numerals
numbers. The Mayan system was based on 20. in Arabic numerals.Have the students look at
The symbol on the bottom shows the 1’s place, the next symbol shows the number of place values to find the value of
the 20’s place, the next symbol shows the 360’s place, the next symbol each number.
shows the 7,200’s place, and so on.
3. Check Point
20’s place 2 20 = 40 Have the students compare the Ancient
1’s place 6 1=6
40 + 6 = 46 numerals and the Arabic numerals we use
46 1 360 = 360 today. Ask them why they think Arabic
0
0 numerals have lasted the longest and are the
360 360 + 0 + 0 = 360 most widely spread number system.
Why Arabic numerals are used today:
6 20 = 120 1. 10 digits
6 1=6
126 120 + 6 = 126 Arabic numbers do not change symbols at
every place value and use a combination of
the digits 0~9 to represent different values.
This is more convenient than other Ancient
Write the Mayan numerals in Arabic numerals. numerals.
2. Different values at different placements
Numbers written in Egyptian, Greece, and
67 121 Roman numerals do not change with
3 20 + 7 1 = 67 6 20 + 1 1 = 121
placement, yet Arabic numerals have a
different value when placed in different
locations.
3. 0 (zero)
Refer to .
3. Ancient Numerals 29 The Arabic number system is used all over the
world because of these reasons.
In the 6th century, “0” was not only used to fill in the empty space, but was used to represent that nothing
was present.
A system of numbers that only represented what was there was changed by “0,” which represented that
nothing was there and the course of Science, Mathematics, and much more. The addition of zero created a
much more efficient number system.
4A Unit 03 043