Page 292 - FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTER
P. 292
NPP
292 Fundamentals of Computers NPP
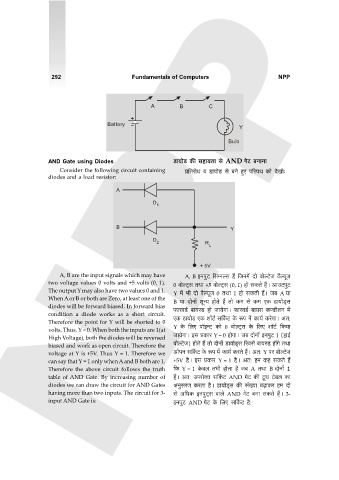
A B C
Battery
Y
Bulb
AND Gate using Diodes S>m`moS> H$s ghm`Vm go AND JoQ> ~ZmZm
Consider the following circuit containing à{VamoY d S>m`moS> go ~Zo hþE n[anW H$mo XoImo…
diodes and a load resistor:
A
D
1
B Y
D 2 R
L
+ 5V
A, B are the input signals which may have A, B BZnwQ> {g½Zëg h¢ {OZ_| Xmo dmoëQ>oO d¡ë`yO
two voltage values 0 volts and +5 volts (0, 1). 0 dmoëQ²>g VWm +5 dmoëQ²>g (0, 1) hmo gH$Vo h¢Ÿ& AmCQ>nwQ>
The output Y may also have two values 0 and 1. Y _| ^r Xmo d¡ë`yO 0 VWm 1 hmo gH$Vr h¢Ÿ& O~ A `m
When A or B or both are Zero, at least one of the B `m XmoZm| eyÝ` hmoVo h¢ Vmo H$_ go H$_ EH$ S>m`moS²>g
diodes will be forward biased. In forward bias \$madS>© ~m`ñS> hmo Om`oJmŸ& \$madS>© ~m`g H$ÊS>reZ _|
condition a diode works as a short circuit.
Therefore the point for Y will be shorted to 0 EH$ S>m`moS> EH$ em°Q>© g{H©$Q> Ho$ ê$n _| H$m`© H$aoJmŸ& AV:
volts. Thus, Y = 0. When both the inputs are 1(at Y Ho$ {bE nm°BÝQ> H$mo 0 dmoëQ²>g Ho$ {bE em°Q>© {H$`m
High Voltage), both the diodes will be reversed Om`oJmŸ& Bg àH$ma Y = 0 hmoJmŸ& O~ XmoZm| BZnwQ> 1 (hmB©
biased and work as open circuit. Therefore the dmoëQ>oO) hmoVo h¢ Vmo XmoZm| S>m`moS²>g [adg© ~m`ñS> hm|Jo VWm
voltage at Y is +5V. Thus Y = 1. Therefore we AmonZ g{H©$Q> Ho$ ê$n _| H$m`© H$aVo h¢Ÿ& AV: Y na dmoëQ>oO
can say that Y = 1 only when A and B both are 1. +5V h¡Ÿ& Bg àH$ma Y = 1 h¡Ÿ& AV: h_ H$h gH$Vo h¢
Therefore the above circuit follows the truth {H$ Y = 1 Ho$db V^r hmoVm h¡ O~ A VWm B XmoZm| 1
table of AND Gate. By increasing number of h¢Ÿ& AV: CnamoŠV g{H©$Q> AND JoQ> H$s Q¯>W Q>o~b H$m
diodes we can draw the circuit for AND Gates AZwgaU H$aVm h¡Ÿ& S>m`moS²>g H$s g§»`m ~‹T>mH$a h_ Xmo
having more than two inputs. The circuit for 3- go A{YH$ BZnwQ²>g dmbo AND JoQ> ~Zm gH$Vo h¢Ÿ& 3-
input AND Gate is: BZnwQ> AND JoQ> Ho$ {bE g{H©$Q> h¡: