Page 270 - 00. Complete Version - Progress Report IPEN 2014-2016
P. 270
270 Nuclear Reactors and Fuel Cycle | Progress Report
Use in Radiotherapy
The objective of this project is to evaluate the
accuracy of the MOSFETS response correction
model, which is usually based on the energy
dependence equation, and eventually propose
modifications by inserting a correction that
takes into account not only the average ener-
gy value of the photons in the target volume,
but also the energy spectrum of the photons.
Evaluations of differences in dose estimation
resulting from this new methodology will be
performed in clinical cases in brachytherapy
and compared with data from planning sys-
tems. This project received funding from the
Universal Call - MCTI / CNPq n.14 / 2014.
Nanofluids Applications in
Nuclear Engineering
This research proj-
ect aims to inves-
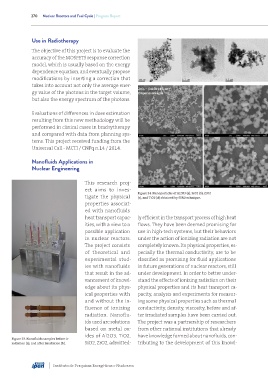
Figure 24. Nanoparticles of Al2O3 (a), SiO2 (b), ZrO2
tigate the physical (c), and TiO2 (d) obtained by SEM technique.
properties associat-
ed with nanofluids
heat transport capac- ly efficient in the transport process of high heat
ities, with a view to a flows. They have been deemed promising for
possible application use in high-tech systems, but their behaviors
in nuclear reactors. under the action of ionizing radiation are not
The project consists completely known. Its physical properties, es-
of theoretical and pecially the thermal conductivity, are to be
experimental stud- classified as promising for fluid applications
ies with nanofluids in future generations of nuclear reactors, still
that result in the ad- under development. In order to better under-
vancement of knowl- stand the effects of ionizing radiation on their
edge about its phys- physical properties and its heat transport ca-
ical properties with pacity, analysis and experiments for measur-
and without the in- ing some physical properties such as thermal
fluence of ionizing conductivity, density, viscosity, before and af-
radiation. Nanoflu- ter irradiated samples have been carried out.
ids used are solutions The project was a partnership of researchers
based on metal ox- from other national institutions that already
ides of Al2O3, TiO2, have knowledge formed about nanofluids, con-
Figure 23. Nanofluids samples before ir-
radiation (a), and after irradiation (b). SiO2, ZrO2, admitted- tributing to the development of this knowl-
Instituto de Pesquisas Energéticas e Nucleares