Page 297 - 00. Complete Version - Progress Report IPEN 2014-2016
P. 297
Materials and Nanotechnology | Progress Report 297
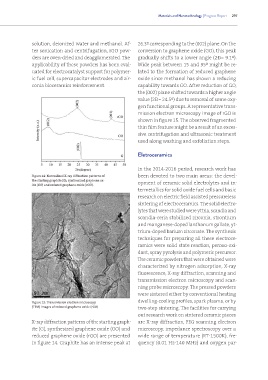
solution, deionized water and methanol. Af- 26.3º corresponding to the (002) plane. On the
ter sonication and centrifugation, rGO pow- conversion to graphene oxide (GO), this peak
ders are oven-dried and deagglomerated. The gradually shifts to a lower angle (2ο= 9.1º).
applicability of these powders has been eval- Wide peak between 15 and 35º might be re-
uated for electrocatalyst support for polymer- lated to the formation of reduced graphene
ic fuel cell, supercapacitor electrodes and zir- oxide since methanol has shown a reducing
conia bioceramics reinforcement. capability towards GO. After reduction of GO,
the (002) plane shifted towards a higher angle
value (2ο= 24.5º) due to removal of some oxy-
gen functional groups. A representative trans-
mission electron microscopy image of rGO is
shown in figure 15. The observed fragmented
thin film feature might be a result of an exces-
sive centrifugation and ultrasonic treatment
used along washing and exfoliation steps.
Eletroceramics
In the 2014-2016 period, research work has
Figure 14: Normalized X-ray diffraction patterns of been devoted to two main areas: the devel-
the starting graphite (G), synthesized graphene ox- opment of ceramic solid electrolytes and in-
ide (GO) and reduced graphene oxide (rGO).
termetallics for solid oxide fuel cells and basic
research on electric field assisted pressureless
sintering of electroceramics. The solid electro-
lytes that were studied were yttria, scandia and
scandia-ceria stabilized zirconia, strontium
and manganese-doped lanthanum gallate, yt-
trium-doped barium zirconate. The synthesis
techniques for preparing all these electroce-
ramics were solid state reaction, peroxo-oxi-
dant, spray pyrolysis and polymeric precursor.
The ceramic powders that were obtained were
characterized by nitrogen adsorption, X-ray
fluorescence, X-ray diffraction, scanning and
transmission electron microscopy and scan-
ning probe microscopy. The pressed powders
were sintered either by conventional heating
dwelling-cooling profiles, spark plasma, or by
Figure 15: Transmission electron microscopy
(TEM) images of reduced graphene oxide (rGO) two-step sintering. The facilities for carrying
out research work on sintered ceramic pieces
X-ray diffraction patterns of the starting graph- are X-ray diffraction, FEG scanning electron
ite (G), synthesized graphene oxide (GO) and microscopy, impedance spectroscopy over a
reduced graphene oxide (rGO) are presented wide range of temperature (RT-1500K), fre-
in figure 14. Graphite has an intense peak at quency (0.01 Hz-140 MHz) and oxygen par-