Page 293 - 00. Complete Version - Progress Report IPEN 2014-2016
P. 293
Materials and Nanotechnology | Progress Report 293
The results indicate that the sigmoidal behav- Y-TZP composites are also promising dental
ior of phase transformation during hydrother- materials that have been studied in our labo-
mal aging, described in the literature, was a ratory. Alumina, for example, can form a phys-
consequence of the limitation of X-ray depth ical barrier against low temperature degra-
penetration during X-ray diffraction analysis dation, with hardness increasing, despite the
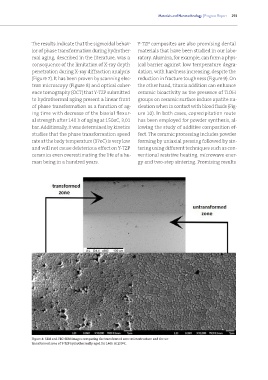
(Figure 7). It has been proven by scanning elec- reduction in fracture toughness (Figure 9). On
tron microscopy (Figure 8) and optical coher- the other hand, titania addition can enhance
ence tomography (OCT) that Y-TZP submitted ceramic bioactivity as the presence of TiOH
to hydrothermal aging present a linear front groups on ceramic surface induce apatite nu-
of phase transformation as a function of ag- cleation when in contact with blood fluids (Fig-
ing time with decrease of the biaxial flexur- ure 10). In both cases, coprecipitation route
al strength after 140 h of aging at 150oC, 3,01 has been employed for powder synthesis, al-
bar. Additionally, it was determined by kinetics lowing the study of additive composition ef-
studies that the phase transformation speed fect. The ceramic processing includes powder
rate at the body temperature (37oC) is very low forming by uniaxial pressing followed by sin-
and will not cause deleterious effect on Y-TZP tering using different techniques such as con-
ceramics even overestimating the life of a hu- ventional resistive heating, microwave ener-
man being in a hundred years. gy and two-step sintering. Promising results
Figure 8: SEM and FEG-SEM images comparing the transformed zone microstructure and the un-
transformed zone of Y-TZP hydrothermally aged for 140h at 150ºC.