Page 294 - 00. Complete Version - Progress Report IPEN 2014-2016
P. 294
294 Materials and Nanotechnology | Progress Report
have been observed with the addition of 10- several surface modifications including me-
20wt% of alumina and 10-30wt% of titania. chanical treatment, thermal spraying, sol–gel
coatings, chemical and electrochemical treat-
ment, ion implantation, and so on.
When a biomaterial has the first contact with
the body, its surface adsorbs proteins from
blood and interstitial fluids. The inflamma-
tory response depends on this formed layer
of proteins, which will determine the activa-
tion of coagulation cascade, complement sys-
tem, platelets and immune cells. Depending
on the cellular and immune responses at the
implantation site of biomaterials, rejection or
degradation of the implant may take place. The
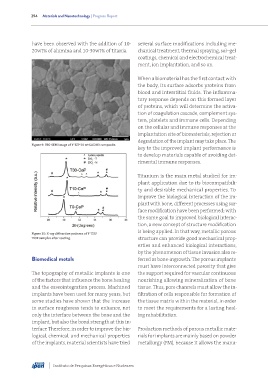
Figure 9: FEG-SEM image of Y-TZP-20 wt%Al2O3 composite.
key to the improved implant performance is
to develop materials capable of avoiding det-
rimental immune responses.
Titanium is the main metal studied for im-
plant application due to its biocompatibili-
ty and desirable mechanical properties. To
improve the biological interaction of the im-
plant with bone, different processes using sur-
face modification have been performed; with
the same goal to improved biological interac-
tion, a new concept of structure modification
is being applied. In that way, metallic porous
Figure 10: X-ray diffraction patterns of Y-TZP/
TiO2 samples after coating. structure can provide good mechanical prop-
erties and enhanced biological interactions,
by the phenomenon of tissue invasion also re-
Biomedical metals ferred as bone-ingrowth. The porous implants
must have interconnected porosity that give
The topography of metallic implants is one the support required for vascular continuous
of the factors that influence the bone healing nourishing allowing mineralization of bone
and the osseointegration process. Machined tissue. Thus, pore channels must allow the in-
implants have been used for many years, but filtration of cells responsible for formation of
some studies have shown that the increase the tissue matrix within the material, in order
in surface roughness tends to enhance, not to meet the requirements for a lasting heal-
only the interface between the bone and the ing rehabilitation.
implant, but also the bond strength at this in-
terface Therefore, in order to improve the bio- Production methods of porous metallic mate-
logical, chemical, and mechanical properties rials for implants are mainly based on powder
of the implants, material scientists have tried metallurgy (PM), because it allows the manu-
Instituto de Pesquisas Energéticas e Nucleares