Page 9 - 03 Cotton SA February 2014
P. 9
Navorsing - Research
eff ect of moisture stress due to hotter temperatures.Facts
A very critical time in crop
management This Week
January: A very critical time in Crop
bove average temperatures across the summer months have Physiological shed can occur late in the season when the plants ‘cut out’, or
Management
th
put this season’s crop development ahead of the previous two. at any time when a stress limits the carbohydrate supply. Be mindful of the
10 Jan 2014
AMeaning that the month of January plays a major role in making or
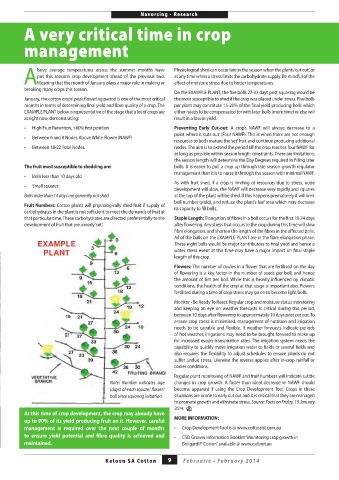
breaking many crops this season. On the EXAMPLE PLANT, the fi ve bolls 27-33 days post squaring would be
Compiled by the CSD Extension and Development Team
the most susceptible to shed if the crop was placed under stress. Five bolls
January, the cotton crops’ peak fl owering period is one of the most critical per plant may constitute 15-20% of the fi nal yield producing bolls which On Friday
months in terms of determining fi nal yield and fi bre quality of a crop. The
X
EXAMPLE PLANT below is representative of the stage that a lot of crops are either needs to be compensated for with later bolls (more time) or else will
Preventing Early Cut-out: A crop's NAWF will always decrease to a
January: A very Critical Time in Crop Management.
at right now, demonstrating: result in a loss in yield.
point where it ‘cuts out’ (Four NAWF). This is when there are not
Above average temperatures across the summer months have
• High Fruit Retention, >80% fi rst position Preventing Early Cut-out: A crop’s NAWF will always decrease to a
enough resources to both mature the ‘set’ fruit and continue
put this season’s crop development ahead of the previous two.
• Between 6 and 8 Nodes Above White Flower (NAWF) point where it ‘cuts out’ (Four NAWF). This is when there are not enough
producing additional nodes. The aim is to extend the period till the
resources to both mature the ‘set’ fruit and continue producing additional
Meaning that the month of January will play a major role in
• Between 18-22 Total Nodes. nodes. The aim is to extend the period till the crop reaches four NAWF for
crop reaches four NAWF for as long as possible within season length
making or breaking many crops this season as long as possible within season length constraints. There are limitations;
constraints. There are limitations; the season length will determine
the season length will determine the Day Degrees required in fi lling later
January, the cotton crops' peak flowering period is one of the
The fruit most susceptible to shedding are: bolls. It is easier to pull a crop up through late season growth regulator
the Day Degrees required in filling later bolls. It is easier to pull a crop
most critical months in terms of determining final yield and fibre
up through late season growth regulator management than it is to
• Bolls less than 10 days old management than it is to nurse it through the season with minimal NAWF.
quality of a crop. The EXAMPLE PLANT below is representative
nurse it through the season with minimal NAWF.
• Small squares As with fruit shed, if a crop is limiting of resources due to stress, node
development will slow, the NAWF will decrease very rapidly and squares
of the stage that a lot of crops are at right now, demonstrating:
As with fruit shed, if a crop is limiting of resources due to stress, node
Bolls older than 14 days are generally not shed. at the top of the plant will be shed. If this happens prematurely it will limit
development will slow, the NAWF will decrease very rapidly and
•
High Fruit Retention, >80% first position
Fruit Numbers: Cotton plants will physiologically shed fruit if supply of boll number (yield), and reduce the plant’s leaf area which may decrease
its capacity to fi ll bolls.
•
Between 6 and 8 Nodes Above White Flower (NAWF)
carbohydrates in the plant is not suffi cient to meet the demands of fruit at squares at the top of the plant will be shed. If this happens
that particular time. These carbohydrates are directed preferentially to the Staple Length: Elongation of fi bres in a boll occurs for the fi rst 18-24 days
prematurely it will limit boll number (yield), and reduce the plant’s leaf
•
Between 18-22 Total Nodes.
development of fruit that are already ‘set’. after fl owering. Any stress that occurs to the crop during this time will slow
area which may decrease its capacity to fill bolls.
fi bre elongation, and shorten the length of the fi bres in the aff ected bolls.
All of the bolls on the EXAMPLE PLANT are in the fi bre elongation phase.
EXAMPLE At this time of crop Staple Length: Elongation of fibres in a boll occurs for the first 18-24
These eight bolls would be major contributors to fi nal yield and hence a
water stress event at this time may have a major impact on fi nal staple
PLANT development, the days after flowering. Any stress that occurs to the crop during this
length of this crop.
crop may already time will slow fibre elongation, and shorten the length of the fibres in
have up to 90% of its the affected bolls. All of the bolls on the EXAMPLE PLANT are in the
Flowers: The number of ovules in a fl ower that are fertilised on the day
of fl owering is a key factor in the number of seeds per boll, and hence
yield producing fruit fibre elongation phase. These eight bolls would be major contributors
the amount of lint per boll. While this is heavily infl uenced by climatic
on it. to final yield and hence a water stress event at this time may have a
conditions, the health of the crop at that stage is important also. Flowers
major impact on final staple length of this crop.
fertilised during a time of crop stress may go on to become light bolls.
However, careful Flowers: The number of ovules in a flower that are fertilised on the
Monitor - Be Ready To React: Regular crop and moisture status monitoring
and keeping an eye on weather forecasts is critical during this period,
management is day of flowering is a key factor in the number of seeds per boll, and
between 10 days after fl owering to approximately 10 days post cut out. To
required over the next hence the amount of lint per boll. While this is heavily influenced by
ensure crop stress is minimised, management of nutrition and irrigation
couple of months to climatic conditions, the health of the crop at that stage is important
needs to be capable and fl exible. If weather forecasts indicate periods
of hot weather, irrigations may need to be brought forward to make up
ensure yield potential also. Flowers fertilised during a time of crop stress may go on to
for increased evapo-transpiration rates. The irrigation system needs the
and fibre quality is become light bolls.
capability to quickly move irrigation water to fi elds or several fi elds and
also requires the fl exibility to adjust schedules to ensure plants do not
achieved and
suff er undue stress. Likewise the reverse applies after in-crop rainfall or
maintained. Monitor - Be Ready To React:
cooler conditions.
Regular crop and moisture status monitoring and keeping an eye on
Regular plant monitoring of NAWF and fruit numbers will indicate subtle
weather forecasts is critical during this period, between 10 days after
Note: Number indicates age (days) of
Note: Number indicates age changes in crop growth. A faster than ideal decrease in NAWF should
flowering to approximately 10 days post cut out.
each square/ flower/ boll since squaring
(days) of each square/ fl ower/ become apparent if using the Crop Development Tool. Crops in these
situations are prone to early cut out and it is critical that they are managed
boll since squaring initiation. initiation.
To ensure crop stress is minimised, management of nutrition and
to promote growth and eliminate stress. Source: Facts on Friday, 10 January
2014.
Fruit Numbers: Cotton plants will physiologically shed fruit if supply
At this time of crop development, the crop may already have irrigation needs to be capable and flexible. If weather forecasts
up to 90% of its yield producing fruit on it. However, careful MORE INFORMATION: indicate periods of hot weather, irrigations may need to be brought
of carbohydrates in the plant is not sufficient to meet the demands of
forward to make up for increased evapo-transpiration rates. The
management is required over the next couple of months • Crop Development Tool is @ www.cottassist.com.au
fruit at that particular time. These carbohydrates are directed
to ensure yield potential and fi bre quality is achieved and • CSD Grower Information Booklet “Monitoring crop growth in tem needs the capability to quickly move irrigation water
irrigation sys
preferentially to the development of fruit that are already ‘set’.
maintained. BollgardII® Cotton” available @ www.csd.net.au
to fields or several fields and also requires the flexibility to adjust
Physiological shed can occur late in the season when the plants ‘cut schedules to ensure plants do not suffer undue stress. Likewise the
out’, or at any time when a stress limits the carbohydrate supply. Be reverse applies after in-crop rainfall or cooler conditions.
9
Februarie • February 2014
Katoen SA Cotton
mindful of the effect of moisture stress due to hotter temperatures Regular plant monitoring of NAWF and fruit numbers will indicate
The fruit most susceptible to shedding are: subtle changes in crop growth. A faster than ideal decrease in NAWF
• Bolls less than 10 days old should become apparent if using the Crop Development Tool. Crops
• Small squares in these situations are prone to early cut out and it is critical that they
Bolls older than 14 days are generally not shed. are managed to promote growth and eliminate stress.
On the EXAMPLE PLANT, the five bolls 27-33 days post squaring MORE INFORMATION:
would be the most susceptible to shed if the crop was placed under
stress. Five bolls per plant may constitute 15-20% of the final yield • Crop Development Tool is @ www.cottassist.com.au
producing bolls which either needs to be compensated for with later • CSD Grower Information Booklet “Monitoring crop growth in
bolls (more time) or else will result in a loss in yield. BollgardII® Cotton” available @ www.csd.net.au
Contacting the CSD Extension and Development Team Sicot, Sicala, Siokra and Sipima cotton varieties are a result
Hay Jorian Millyard 0428 950009 Moree James Quinn 0428 950028 of a research program conducted by CSIRO.
Wee Waa Bob Ford 0428 950015 Goondiwindi Alex North 0428 950021 Supported by the Cotton Research & Development
Narrabri Rob Eveleigh 0427 915921 Dalby John Marshall 0428 950010 Corporation until 2006
Cotton Seed Distributors Ltd. Is a major contributor to the CottonInfo Team. ® Registered Trademark of Monsanto LLC, ® Registered Trademark of Bayer