Page 426 - Cambridge IGCSE Business Studies
P. 426
IGCSE Business Studies Student CD-ROM
16 Costs, scale of production and break-even analysis
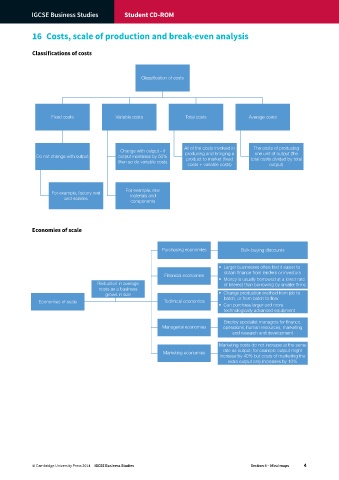
Classifications of costs
Classification of costs
Fixed costs Variable costs Total costs Average costs
All of the costs involved in The costs of producing
Change with output – if producing and bringing a one unit of output (the
Do not change with output output increases by 50% product to market (fixed total costs divided by total
then so do variable costs
costs + variable costs) output)
For example, raw
For example, factory rent materials and
and salaries
components
Economies of scale
Purchasing economies Bulk-buying discounts
• Larger businesses often find it easier to
obtain finance from lenders or investors
Financial economies
• Money is usually borrowed at a lower rate
Reduction in average of interest than borrowing by smaller firms
costs as a business
grows in size • Change production method from job to
Economies of scale Technical economies batch, or from batch to flow
• Can purchase larger and more
technologically advanced equipment
Employ specialist managers for finance,
Managerial economies operations, human resources, marketing
and research and development
Marketing costs do not increase at the same
Marketing economies rate as output; for example output might
increase by 40% but costs of marketing the
extra output only increases by 10%
© Cambridge University Press 2014 IGCSE Business Studies Section 4 – Mind maps 4