Page 108 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 108
P1: FAW
BLUK007-03 BLUK007-Kendall May 25, 2005 17:29 Char Count= 0
104 Chapter 3: Respiratory system
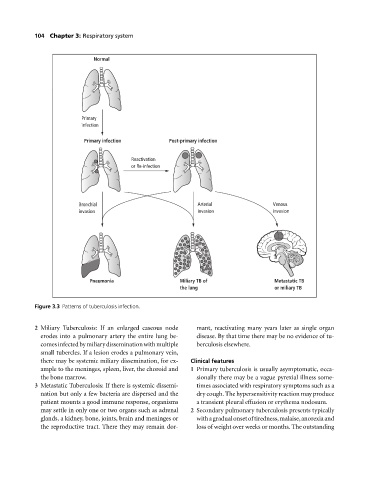
Normal
Primary
infection
Primary infection Post-primary infection
Reactivation
or Re-infection
Bronchial Arterial Venous
invasion invasion invasion
Pneumonia Miliary TB of Metastatic TB
the lung or miliary TB
Figure 3.3 Patterns of tuberculosis infection.
2 Miliary Tuberculosis: If an enlarged caseous node mant, reactivating many years later as single organ
erodes into a pulmonary artery the entire lung be- disease. By that time there may be no evidence of tu-
comesinfectedbymiliarydisseminationwithmultiple berculosis elsewhere.
small tubercles. If a lesion erodes a pulmonary vein,
there may be systemic miliary dissemination, for ex- Clinical features
ample to the meninges, spleen, liver, the choroid and 1 Primary tuberculosis is usually asymptomatic, occa-
the bone marrow. sionally there may be a vague pyrexial illness some-
3 Metastatic Tuberculosis: If there is systemic dissemi- times associated with respiratory symptoms such as a
nation but only a few bacteria are dispersed and the dry cough. The hypersensitivity reaction may produce
patient mounts a good immune response, organisms atransient pleural effusion or erythema nodosum.
may settle in only one or two organs such as adrenal 2 Secondary pulmonary tuberculosis presents typically
glands, a kidney, bone, joints, brain and meninges or withagradualonsetoftiredness,malaise,anorexiaand
the reproductive tract. There they may remain dor- loss of weight over weeks or months. The outstanding