Page 104 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 104
P1: FAW
BLUK007-03 BLUK007-Kendall May 25, 2005 17:29 Char Count= 0
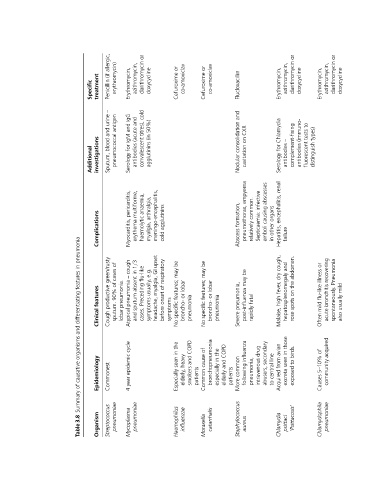
allergic, (if or or or or or
Specific treatment Penicillin erythromycin) Erythromycin, azithromycin, clarithromycin doxycycline Cefuroxime co-amoxiclav Cefuroxime co-amoxiclav Flucloxacillin Erythromycin, azithromycin, clarithromycin doxycycline Erythromycin, azithromycin, clarithromycin doxycycline
– cold and
urine antigen IgG and to
and blood and IgM (acute titres), 50%) (in consolidation CXR on Chlamydia – (immuno- tests types)
Additional investigations Sputum, pneumococcal for Serology antibodies convalescent agglutinins Nodular cavitation for Serology antibodies complement-fixing antibodies fluorescent distinguish
pericarditis, multiforme, anaemia, arthralgia, meningo-encephalitis, formation, empyema common. infective abscesses causing organs renal encephalitis,
Complications Myocarditis, erythema haemolytic myalgia, agglutinins cold Abscess pneumothorax, relatively Septicaemia: emboli other in Hepatitis, failure
pneumonia
in green/rusty of cough 1/3 in e.g. upset GI respiratory be may be may be cough, and abdomen. or recovering Pneumonia
features cases of 90% pneumonia. – pneumonia absent flu-like Preceding usually, myalgia, of features; lobar features; lobar may dry fever, the on illness flu-like mild
differentiating features Clinical productive Cough sputum. lobar Atypical sputum and cases. symptoms headache, onset before symptoms specific or broncho- pneumonia specific or broncho- pneumonia pneumonia, Severe post-influenza fatal rapidly high Malaise, hepatosplenomegaly spots rose mild bronchitis acute spontaneously. usually also
and No No Often
organisms cycle the in COPD and of the in COPD influenza drug secondary line avian those in birds. of acquired
causative Epidemiology Commonest epidemic seen heavy elderly, smokers patients cause bronchopneumonia especially and elderly patients common following pneumonia, intravenous abusers, central from seen excreta to exposed 5–10% community
of year 4 Especially Common More to Acquired Causes
Summary
Table 3.8 Organism Streptococcus pneumoniae Mycoplasma pneumoniae Haemophilus influenzae Moraxella catarrhalis Staphylococcus aureus Chlamydia psittaci ‘Psittacosis’ Chlamydophila pneumoniae
100