Page 229 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 229
P1: KPE
BLUK007-06 BLUK007-Kendall May 25, 2005 18:6 Char Count= 0
Chapter 6: Clinical 225
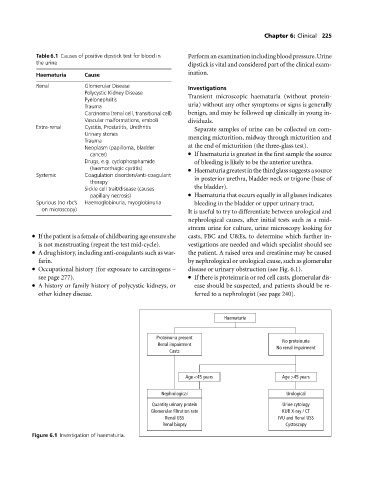
Table 6.1 Causes of positive dipstick test for blood in Performanexaminationincludingbloodpressure.Urine
the urine dipstick is vital and considered part of the clinical exam-
Haematuria Cause ination.
Renal Glomerular Disease Investigations
Polycystic Kidney Disease
Pyelonephritis Transient microscopic haematuria (without protein-
Trauma uria) without any other symptoms or signs is generally
Carcinoma (renal cell, transitional cell) benign, and may be followed up clinically in young in-
Vascular malformations, emboli dividuals.
Extra-renal Cystitis, Prostatitis, Urethritis Separate samples of urine can be collected on com-
Urinary stones mencing micturition, midway through micturition and
Trauma
Neoplasm (papilloma, bladder at the end of micturition (the three-glass test).
cancer) If haematuria is greatest in the first sample the source
Drugs, e.g. cyclophosphamide of bleeding is likely to be the anterior urethra.
(haemorrhagic cystitis) Haematuriagreatestinthethirdglasssuggestsasource
Systemic Coagulation disorders/anti-coagulant in posterior urethra, bladder neck or trigone (base of
therapy
Sickle cell trait/disease (causes the bladder).
papillary necrosis) Haematuria that occurs equally in all glasses indicates
Spurious (no rbc’s Haemoglobinuria, myoglobinuria bleeding in the bladder or upper urinary tract.
on microscopy) It is useful to try to differentiate between urological and
nephrological causes, after initial tests such as a mid-
stream urine for culture, urine microscopy looking for
If the patient is a female of childbearing age ensure she casts, FBC and U&Es, to determine which further in-
is not menstruating (repeat the test mid-cycle). vestigations are needed and which specialist should see
Adrug history, including anti-coagulants such as war- the patient. A raised urea and creatinine may be caused
farin. by nephrological or urological cause, such as glomerular
Occupational history (for exposure to carcinogens – disease or urinary obstruction (see Fig. 6.1).
see page 277). If there is proteinuria or red cell casts, glomerular dis-
A history or family history of polycystic kidneys, or ease should be suspected, and patients should be re-
other kidney disease. ferred to a nephrologist (see page 240).
Haematuria
Proteinuria present
Renal impairment No proteinuria
No renal impairment
Casts
Age <45 years Age >45 years
Nephrological Urological
Quantity urinary protein Urine cytology
Glomerular filtration rate KUB X-ray / CT
Renal USS IVU and Renal USS
Renal biopsy Cystoscopy
Figure 6.1 Investigation of haematuria.