Page 451 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 451
P1: FAW
BLUK007-11 BLUK007-Kendall May 25, 2005 8:5 Char Count= 0
Chapter 11: Disorders of the parathyroids 447
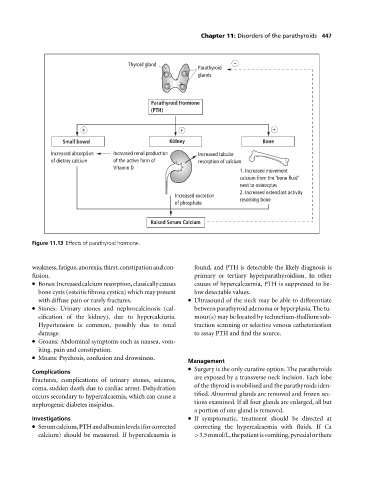
Thyroid gland –
Parathyroid
glands
Parathyroid Hormone
(PTH)
+ + +
Small bowel Kidney Bone
Increased absorption Increased renal production Increased tubular
of dietary calcium of the active form of resorption of calcium
Vitamin D
1. Increased movement
calcium from the 'bone fluid'
next to osteocytes
2. Increased osteoclast activity
Increased excretion resorbing bone
of phosphate
Raised Serum Calcium
Figure 11.13 Effects of parathyroid hormone.
weakness,fatigue,anorexia,thirst,constipationandcon- found, and PTH is detectable the likely diagnosis is
fusion. primary or tertiary hyperparathyroidism. In other
Bones:Increasedcalciumresorption,classicallycauses causes of hypercalcaemia, PTH is suppressed to be-
bone cysts (osteitis fibrosa cystica) which may present low detectable values.
with diffuse pain or rarely fractures. Ultrasound of the neck may be able to differentiate
Stones: Urinary stones and nephrocalcinosis (cal- between parathyroid adenoma or hyperplasia. The tu-
cification of the kidney), due to hypercalciuria. mour(s) may be located by technetium-thallium sub-
Hypertension is common, possibly due to renal traction scanning or selective venous catheterisation
damage. to assay PTH and find the source.
Groans: Abdominal symptoms such as nausea, vom-
iting, pain and constipation.
Moans: Psychosis, confusion and drowsiness.
Management
Surgery is the only curative option. The parathyroids
Complications
are exposed by a transverse neck incision. Each lobe
Fractures, complications of urinary stones, seizures,
of the thyroid is mobilised and the parathyroids iden-
coma, sudden death due to cardiac arrest. Dehydration
tified. Abnormal glands are removed and frozen sec-
occurs secondary to hypercalcaemia, which can cause a
tions examined. If all four glands are enlarged, all but
nephrogenic diabetes insipidus.
aportion of one gland is removed.
Investigations If symptomatic, treatment should be directed at
Serumcalcium,PTHandalbuminlevels(forcorrected correcting the hypercalcaemia with fluids. If Ca
calcium) should be measured. If hypercalcaemia is >3.5mmol/L,thepatientisvomiting,pyrexialorthere