Page 90 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 90
P1: JYS
BLUK007-02 BLUK007-Kendall May 25, 2005 17:25 Char Count= 0
86 Chapter 2: Cardiovascular system
syndrome. The defect is closed, often using a Dacron
patch, under cardiopulmonary bypass.
If the pulmonary hypertension has developed and the
shunt direction has reversed, surgery is contraindi-
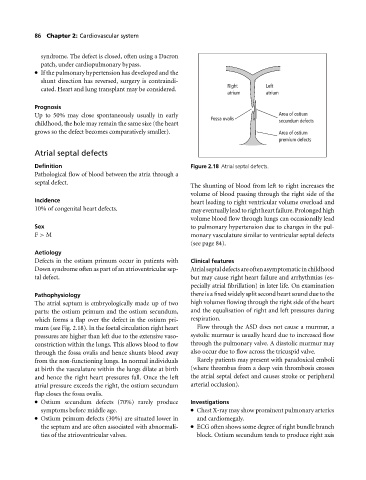
Right Left
cated. Heart and lung transplant may be considered.
atrium atrium
Prognosis
Up to 50% may close spontaneously usually in early Area of ostium
Fossa ovalis secundum defects
childhood, the hole may remain the same size (the heart
growsso the defect becomes comparatively smaller). Area of ostium
premium defects
Atrial septal defects
Definition Figure 2.18 Atrial septal defects.
Pathological flow of blood between the atria through a
septal defect.
The shunting of blood from left to right increases the
volume of blood passing through the right side of the
Incidence heart leading to right ventricular volume overload and
10% of congenital heart defects. mayeventuallyleadtorightheartfailure.Prolongedhigh
volume blood flow through lungs can occasionally lead
Sex to pulmonary hypertension due to changes in the pul-
F > M monary vasculature similar to ventricular septal defects
(see page 84).
Aetiology
Defects in the ostium primum occur in patients with Clinical features
Down syndrome often as part of an atrioventricular sep- Atrialseptaldefectsareoftenasymptomaticinchildhood
tal defect. but may cause right heart failure and arrhythmias (es-
pecially atrial fibrillation) in later life. On examination
Pathophysiology there is a fixed widely split second heart sound due to the
The atrial septum is embryologically made up of two high volumes flowing through the right side of the heart
parts: the ostium primum and the ostium secundum, and the equalisation of right and left pressures during
which forms a flap over the defect in the ostium pri- respiration.
mum (see Fig. 2.18). In the foetal circulation right heart Flow through the ASD does not cause a murmur, a
pressures are higher than left due to the extensive vaso- systolic murmur is usually heard due to increased flow
constriction within the lungs. This allows blood to flow through the pulmonary valve. A diastolic murmur may
through the fossa ovalis and hence shunts blood away also occur due to flow across the tricuspid valve.
from the non-functioning lungs. In normal individuals Rarely patients may present with paradoxical emboli
at birth the vasculature within the lungs dilate at birth (where thrombus from a deep vein thrombosis crosses
and hence the right heart pressures fall. Once the left the atrial septal defect and causes stroke or peripheral
atrial pressure exceeds the right, the ostium secundum arterial occlusion).
flap closes the fossa ovalis.
Ostium secundum defects (70%) rarely produce Investigations
symptoms before middle age. Chest X-ray may show prominent pulmonary arteries
Ostium primum defects (30%) are situated lower in and cardiomegaly.
the septum and are often associated with abnormali- ECG often shows some degree of right bundle branch
ties of the atrioventricular valves. block. Ostium secundum tends to produce right axis