Page 91 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 91
P1: JYS
BLUK007-02 BLUK007-Kendall May 25, 2005 17:25 Char Count= 0
Chapter 2: Congenital heart disease 87
deviation, whereas ostium primum produces left axis Neonatal coarctation is often associated with a patent
deviation. ductus arteriosus in which the high aortic pressures re-
Echocardiogram demonstrates abnormal septal mo- sult in severe left to right shunting and early severe car-
tion and can show blood flow between the atria. diac failure.
Eighty per cent of cases occur in association with a
Management bicuspid aortic valve.
In ostium secundum defect repair is safe and advisable.
The defect may be closed using an umbrella-shaped Clinical features
occluder placed at cardiac catheterisation. Traditional Proximal hypertension may cause headache and dizzi-
open surgical repair requires cardiopulmonary bypass ness, distal hypotension results in weakness and poor pe-
and may use a pericardial or Dacron patch to close the ripheral circulation. On examination the femoral pulses
defect.Surgicalinterventioninostiumprimumdefectsis are weak or absent and there is radiofemoral delay. Four-
morecomplexduetoinvolvementoftheatrioventricular limb blood pressure measurement will demonstrate the
valves. difference between upper and lower body. The flow mur-
muracross the coarctation is best heard at the back.
Coarctation of the aorta
Investigations
Definition
Chest X-ray may show left ventricular hypertrophy
Localised narrowing of the descending aorta close to the
and rib notching due to dilated intercostal arteries
site of the ductus arteriosus.
causing erosion.
Pathophysiology ECG may show left ventricular hypertrophy.
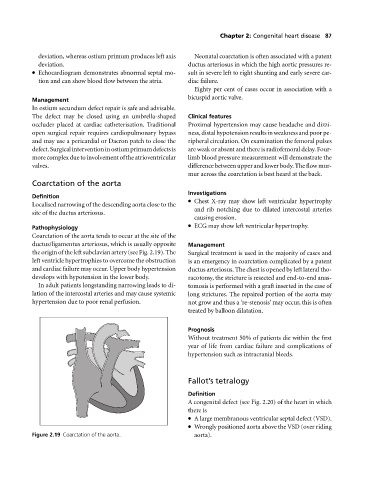
Coarctation of the aorta tends to occur at the site of the
ductus/ligamentus arteriosus, which is usually opposite Management
the origin of the left subclavian artery (see Fig. 2.19). The Surgical treatment is used in the majority of cases and
left ventricle hypertrophies to overcome the obstruction is an emergency in coarctation complicated by a patent
and cardiac failure may occur. Upper body hypertension ductus arteriosus. The chest is opened by left lateral tho-
develops with hypotension in the lower body. racotomy, the stricture is resected and end-to-end anas-
In adult patients longstanding narrowing leads to di- tomosis is performed with a graft inserted in the case of
lation of the intercostal arteries and may cause systemic long strictures. The repaired portion of the aorta may
hypertension due to poor renal perfusion. not grow and thus a ‘re-stenosis’ may occur, this is often
treated by balloon dilatation.
Prognosis
Without treatment 50% of patients die within the first
year of life from cardiac failure and complications of
hypertension such as intracranial bleeds.
Fallot’s tetralogy
Definition
Acongenital defect (see Fig. 2.20) of the heart in which
there is
A large membranous ventricular septal defect (VSD).
Wrongly positioned aorta above the VSD (over riding
Figure 2.19 Coarctation of the aorta. aorta).