Page 95 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 95
P1: FAW
BLUK007-03 BLUK007-Kendall May 25, 2005 17:29 Char Count= 0
Chapter 3: Clinical 91
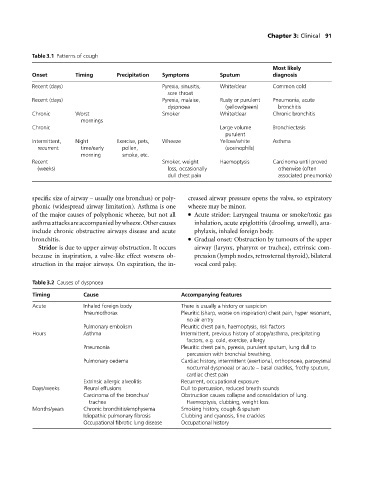
Table 3.1 Patterns of cough
Most likely
Onset Timing Precipitation Symptoms Sputum diagnosis
Recent (days) Pyrexia, sinusitis, White/clear Common cold
sore throat
Recent (days) Pyrexia, malaise, Rusty or purulent Pneumonia, acute
dyspnoea (yellow/green) bronchitis
Chronic Worst Smoker White/clear Chronic bronchitis
mornings
Chronic Large volume Bronchiectasis
purulent
Intermittent, Night Exercise, pets, Wheeze Yellow/white Asthma
recurrent time/early pollen, (eosinophils)
morning smoke, etc.
Recent Smoker, weight Haemoptysis Carcinoma until proved
(weeks) loss, occasionally otherwise (often
dull chest pain associated pneumonia)
specific size of airway – usually one bronchus) or poly- creased airway pressure opens the valve, so expiratory
phonic (widespread airway limitation). Asthma is one wheeze may be minor.
of the major causes of polyphonic wheeze, but not all Acute stridor: Laryngeal trauma or smoke/toxic gas
asthmaattacksareaccompaniedbywheeze.Othercauses inhalation, acute epiglottitis (drooling, unwell), ana-
include chronic obstructive airways disease and acute phylaxis, inhaled foreign body.
bronchitis. Gradual onset: Obstruction by tumours of the upper
Stridor is due to upper airway obstruction. It occurs airway (larynx, pharynx or trachea), extrinsic com-
because in inspiration, a valve-like effect worsens ob- pression (lymph nodes, retrosternal thyroid), bilateral
struction in the major airways. On expiration, the in- vocal cord palsy.
Table 3.2 Causes of dyspnoea
Timing Cause Accompanying features
Acute Inhaled foreign body There is usually a history or suspicion
Pneumothorax Pleuritic (sharp, worse on inspiration) chest pain, hyper resonant,
no air entry
Pulmonary embolism Pleuritic chest pain, haemoptysis, risk factors
Hours Asthma Intermittent, previous history of atopy/asthma, precipitating
factors, e.g. cold, exercise, allergy
Pneumonia Pleuritic chest pain, pyrexia, purulent sputum, lung dull to
percussion with bronchial breathing.
Pulmonary oedema Cardiac history, intermittent (exertional, orthopnoea, paroxysmal
nocturnal dyspnoea) or acute – basal crackles, frothy sputum,
cardiac chest pain
Extrinsic allergic alveolitis Recurrent, occupational exposure
Days/weeks Pleural effusions Dull to percussion, reduced breath sounds
Carcinoma of the bronchus/ Obstruction causes collapse and consolidation of lung.
trachea Haemoptysis, clubbing, weight loss.
Months/years Chronic bronchitis/emphysema Smoking history, cough & sputum
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis Clubbing and cyanosis, fine crackles
Occupational fibrotic lung disease Occupational history