Page 37 - VIRANSH COACHING CLASSES
P. 37
% Q price
Symbolically, Ec = A
% P
B Types of Price Elasticity of Demand :
Q P
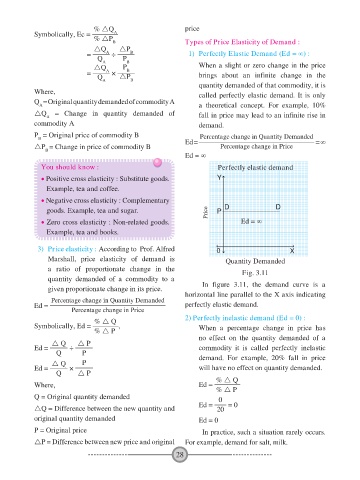
= A ÷ B 1) Perfectly Elastic Demand (Ed = ∞) :
Q A P B
Q P When a slight or zero change in the price
= A × B brings about an infinite change in the
Q P
A B
quantity demanded of that commodity, it is
Where, called perfectly elastic demand. It is only
Q = Original quantity demanded of commodity A
A a theoretical concept. For example, 10%
Q = Change in quantity demanded of fall in price may lead to an infinite rise in
A
commodity A demand.
P = Original price of commodity B Percentage change in Quantity Demanded
B Ed = = ∞
P = Change in price of commodity B Percentage change in Price
B
Ed = ∞
You should know : Perfectly elastic demand
• Positive cross elasticity : Substitute goods. Y
Example, tea and coffee.
• Negative cross elasticity : Complementary
goods. Example, tea and sugar. Price P D D
• Zero cross elasticity : Non-related goods. Ed = ∞
Example, tea and books.
3) Price elasticity : According to Prof. Alfred 0 X
Marshall, price elasticity of demand is Quantity Demanded
a ratio of proportionate change in the Fig. 3.11
quantity demanded of a commodity to a
given proportionate change in its price. In figure 3.11, the demand curve is a
horizontal line parallel to the X axis indicating
Percentage change in Quantity Demanded
Ed = perfectly elastic demand.
Percentage change in Price
% Q 2) Perfectly inelastic demand (Ed = 0) :
Symbolically, Ed = , When a percentage change in price has
% P
no effect on the quantity demanded of a
Q P
Ed = ÷ commodity it is called perfectly inelastic
Q P demand. For example, 20% fall in price
Q P
Ed = × will have no effect on quantity demanded.
Q P
% Q
Where, Ed =
% P
Q = Original quantity demanded 0
Ed = = 0
Q = Difference between the new quantity and 20
original quantity demanded Ed = 0
P = Original price In practice, such a situation rarely occurs.
P = Difference between new price and original For example, demand for salt, milk.
28