Page 40 - VIRANSH COACHING CLASSES
P. 40
` 10 per unit and quantity demanded is 6 units.
2) Price elasticity of demand is a pure
number. It does not depend upon units Therefore, total expenditure incurred is ` 60.
in which price of the commodity and its When price rises to ` 20 quantity demanded falls
quantity are measured. to 5 units, the total expenditure incurred is ` 100.
In this case, total outlay is greater than original
2) Total Expenditure Method : This method expenditure. Hence, in this example elasticity
was developed by Prof. Marshall. In this of demand is greater than one. (Ed >1) that is
method, total amount of expenditure before relatively elastic demand.
and after the price change is compared. In example ‘B’, original price is ` 30 per
unit and quantity demanded is 4 units. Therefore
Here the total expenditure refers to the
product of price and quantity demanded. total expenditure is ` 120. When price rises to
` 40 quantity demanded falls to ‘3’ units. Total
Total expenditure = Price × Quantity demanded
expenditure incurred is ` 120. In this case total
In this connection, Marshall has given the outlay is same (equal) to original expenditure.
following propositions :
Hence, in this example, elasticity of demand
A) Relatively elastic demand (Ed >1) : is equal to one (Ed = 1) that is unitary elastic
When with a given change in the price of a demand.
commodity total outlay increases, elasticity In example ‘C’, original price is ` 50 per
of demand is greater than one. unit and quantity demanded is 2 units. Therefore
B) Unitary elastic demand (Ed = 1) : total expenditure is ` 100. When price rises
When price falls or rises, total outlay does to ` 60, quantity demand falls to 1 unit and
not change or remains constant, elasticity total expenditure incurred is ` 60. In this case
of demand is equal to one. total outlay is less than original expenditure.
C) Relatively inelastic demand (Ed <1) : Hence, elasticity of demand is less than one
When with a given change in price of a (Ed <1) that is relatively inelastic demand.
commodity total outlay decreases, elasticity
of demand is less than one. Find out :
This can be explained with the help of the As the price of peanut packets increases
following example. by 5% the demand for number of peanut
packets falls by 8%. What is the elasticity
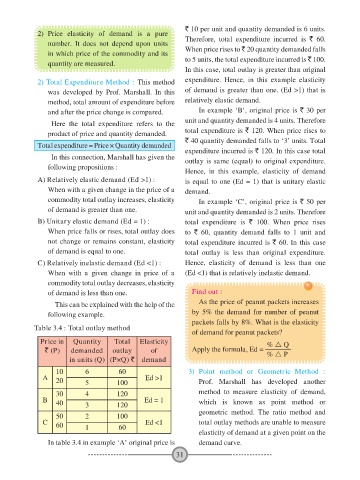
Table 3.4 : Total outlay method
of demand for peanut packets?
Price in Quantity Total Elasticity % Q
` (P) demanded outlay of Apply the formula, Ed = % P
in units (Q) (P×Q) ` demand
10 6 60 3) Point method or Geometric Method :
A 20 5 100 Ed >1 Prof. Marshall has developed another
30 4 120 method to measure elasticity of demand,
B 40 3 120 Ed = 1 which is known as point method or
geometric method. The ratio method and
50 2 100
C 60 1 60 Ed <1 total outlay methods are unable to measure
elasticity of demand at a given point on the
In table 3.4 in example ‘A’ original price is demand curve.
31