Page 42 - VIRANSH COACHING CLASSES
P. 42
Factors influencing the elasticity of demand : 8) Urgency of needs : Goods which are
Elasticity of demand depends upon several urgently needed will have relatively
factors which are discussed below : inelastic demand. For example, medicines.
1) Nature of commodity : By nature we Luxury goods which are less urgent have
can classify commodities as necessaries, relatively elastic demand.
comforts and luxury goods. Demand for 9) Time period : Elasticity of demand is
necessaries like foodgrains, medicines, always related to period of time. It varies
textbooks etc. is relatively inelastic and with the length of time period. Generally
for comforts and luxury goods like cars, speaking, longer the duration of period
perfumes, furniture etc. demand is relatively greater will be the elasticity of demand and
elastic. vice-versa. This is because a consumer can
2) Availability of substitutes : Demand for a change the consumption habits in the long
commodity will be more elastic, if its close run in favour of cheaper substitutes of the
substitutes are available in the market. For commodities.
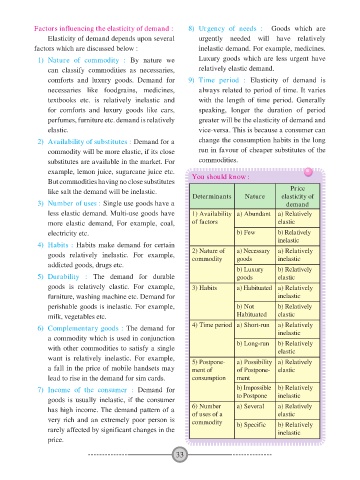
example, lemon juice, sugarcane juice etc. You should know :
But commodities having no close substitutes
like salt the demand will be inelastic. Price
Determinants Nature elasticity of
3) Number of uses : Single use goods have a demand
less elastic demand. Multi-use goods have 1) Availability a) Abundant a) Relatively
more elastic demand, For example, coal, of factors elastic
electricity etc. b) Few b) Relatively
inelastic
4) Habits : Habits make demand for certain
goods relatively inelastic. For example, 2) Nature of a) Necessary a) Relatively
commodity
inelastic
goods
addicted goods, drugs etc.
b) Luxury b) Relatively
5) Durability : The demand for durable goods elastic
goods is relatively elastic. For example, 3) Habits a) Habituated a) Relatively
furniture, washing machine etc. Demand for inelastic
perishable goods is inelastic. For example, b) Not b) Relatively
milk, vegetables etc. Habituated elastic
6) Complementary goods : The demand for 4) Time period a) Short-run a) Relatively
inelastic
a commodity which is used in conjunction b) Long-run b) Relatively
with other commodities to satisfy a single
elastic
want is relatively inelastic. For example, 5) Postpone- a) Possibility a) Relatively
a fall in the price of mobile handsets may ment of of Postpone- elastic
lead to rise in the demand for sim cards. consumption ment
7) Income of the consumer : Demand for b) Impossible b) Relatively
to Postpone inelastic
goods is usually inelastic, if the consumer
has high income. The demand pattern of a 6) Number a) Several a) Relatively
of uses of a
elastic
very rich and an extremely poor person is commodity b) Specific b) Relatively
rarely affected by significant changes in the inelastic
price.
33