Page 77 - Cambridge+Checkpoint+Mathematics+Coursebook+9
P. 77
8.1 Constructing perpendicular lines
8.1 Constructing perpendicular lines
You need to be able to construct the perpendicular from a point The term ‘straight edge’ is used
on a line, and the perpendicular from a point to a line, using only when you are not allowed to use a
a straight edge and compasses. You can use a ruler as the straight ruler to measure lengths. You still
edge, but you must not use a protractor to do these constructions. need to draw straight lines, though.
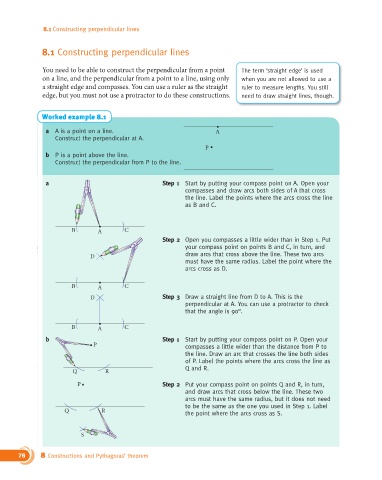
Worked example 8.1
a A is a point on a line. A
Construct the perpendicular at A.
P
b P is a point above the line.
Construct the perpendicular from P to the line.
a Step 1 Start by putting your compass point on A. Open your
compasses and draw arcs both sides of A that cross
the line. Label the points where the arcs cross the line
as B and C.
B A C
Step 2 Open you compasses a little wider than in Step 1. Put
your compass point on points B and C, in turn, and
D draw arcs that cross above the line. These two arcs
must have the same radius. Label the point where the
arcs cross as D.
B A C
D Step 3 Draw a straight line from D to A. This is the
perpendicular at A. You can use a protractor to check
that the angle is 90°.
B A C
b Step 1 Start by putting your compass point on P. Open your
P compasses a little wider than the distance from P to
the line. Draw an arc that crosses the line both sides
of P. Label the points where the arcs cross the line as
Q and R.
Q R
P Step 2 Put your compass point on points Q and R, in turn,
and draw arcs that cross below the line. These two
arcs must have the same radius, but it does not need
to be the same as the one you used in Step 1. Label
Q R the point where the arcs cross as S.
S
76 8 Constructions and Pythagoras’ theorem
76