Page 78 - Cambridge+Checkpoint+Mathematics+Coursebook+9
P. 78
8.1 Constructing perpendicular lines
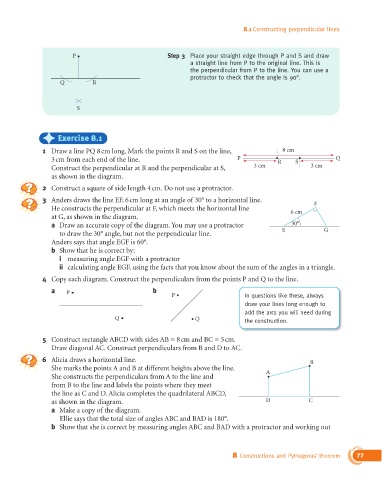
P Step 3 Place your straight edge through P and S and draw
a straight line from P to the original line. This is
the perpendicular from P to the line. You can use a
protractor to check that the angle is 90°.
Q R
S
) Exercise 8.1
1 Draw a line PQ 8 cm long. Mark the points R and S on the line, 8 cm
3 cm from each end of the line. P R S Q
Construct the perpendicular at R and the perpendicular at S, 3 cm 3 cm
as shown in the diagram.
2 Construct a square of side length 4 cm. Do not use a protractor.
3 Anders draws the line EF, 6 cm long at an angle of 30° to a horizontal line. F
He constructs the perpendicular at F, which meets the horizontal line 6 cm
at G, as shown in the diagram.
a Draw an accurate copy of the diagram. You may use a protractor 30°
to draw the 30° angle, but not the perpendicular line. E G
Anders says that angle EGF is 60°.
b Show that he is correct by:
i measuring angle EGF with a protractor
ii calculating angle EGF, using the facts that you know about the sum of the angles in a triangle.
4 Copy each diagram. Construct the perpendiculars from the points P and Q to the line.
P
a P b P In questions like these, always
Q draw your lines long enough to
P
add the arcs you will need during
Q Q the construction.
Q
5 Construct rectangle ABCD with sides AB = 8 cm and BC = 5 cm.
Draw diagonal AC. Construct perpendiculars from B and D to AC.
6 Alicia draws a horizontal line. B
She marks the points A and B at different heights above the line. A
She constructs the perpendiculars from A to the line and
from B to the line and labels the points where they meet
the line as C and D. Alicia completes the quadrilateral ABCD,
as shown in the diagram. D C
a Make a copy of the diagram.
Ellie says that the total size of angles ABC and BAD is 180°.
b Show that she is correct by measuring angles ABC and BAD with a protractor and working out
8 Constructions and Pythagoras’ theorem 77