Page 40 - CASA Bulletin 2019 Vol 6 No 4
P. 40
CASA Bulletin of Anesthesiology
DOI: 10.31480/2330-4871/093
or central canals, facet disease after lumbar fixation, or the indication of FBSS or post-laminectomy syndrome.
pain from a persistent surgical scar. These patients typ- The search was conducted using PubMed, Ovid and
ically do not experience much improvement with mul- MEDLINE. MeSH terms included [“failed back surgery
tiple conservative therapies such as oral medications, syndrome” AND neuromodulation], [neuromodulation
physical therapy, and various injections even prior to AND FBSS], [“failed back surgery syndrome” AND
the back surgery. In these cases, persistent pain after “spinal cord stimulation”], [FBSS AND “spinal cord
back surgery can be exponentially difficult to manage. stimulation”], and [“spinal cord stimulation” AND
In this paper, we will systematically review the “post-laminectomy syndrome”]. Studies published
scientific evidence behind spinal cord stimulation with between 1991 and 2018 were included. A total of 677
a focus on patient selection considerations for the studies were identified through a PubMed search. Four
indication of failed back surgery syndrome. more studies were identified through the citations of
relevant aforementioned studies. The studies were
Methods further narrowed by screening for clinical studies and
A) Search Strategy removing duplicates. After applying the stated inclusion
and exclusion criteria and removing two studies with
A literature search was conducted by the authors
to identify randomized controlled trials and matched missing data, 11 studies were ultimately included in our
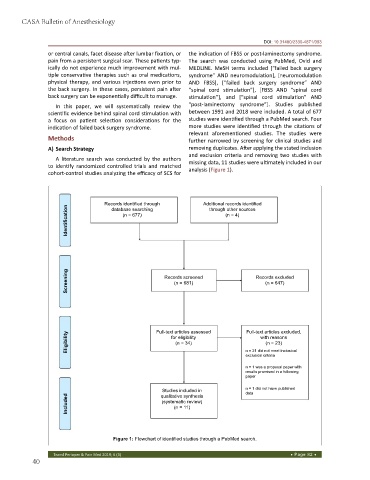
analysis (Figure 1).
cohort-control studies analyzing the efficacy of SCS for
Records identified through Additional records identified
Identification (n = 677) (n = 4)
through other sources
database searching
Screening Records screened Records excluded
(n = 681)
(n = 647)
Eligibility Full-text articles assessed Full-text articles excluded,
with reasons
for eligibility
(n = 23)
(n = 34)
n = 21 did not meet inclusion/
exclusion criteria
n = 1 was a proposal paper with
results promised in a following
paper
Studies included in n = 1 did not have published
data
qualitative synthesis
Included (systematic review)
(n = 11)
Figure 1: Flowchart of identified studies through a PubMed search.
Transl Perioper & Pain Med 2019; 6 (3) • Page 82 •
40