Page 191 - [Uma_Sekaran]_Research_methods_for_business__a_sk(BookZZ.org)
P. 191
HOW VARIABLES ARE MEASURED 175
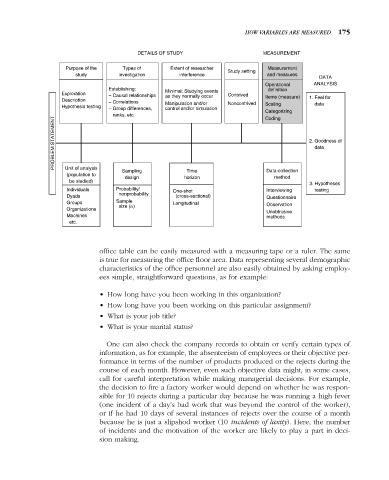
DETAILS OF STUDY MEASUREMENT
Purpose of the Types of Extent of researcher Measurement
Study setting
study investigation interference and measures
DATA
Operational ANALYSIS
Establishing: definition
Exploration Minimal: Studying events
– Causal relationships as they normally occur Contrived Items (measure)
Description 1. Feel for
– Correlations Manipulation and/or Noncontrived
Hypothesis testing Scaling data
– Group differences, control and/or simulation
Categorizing
ranks, etc. Coding
PROBLEM STATEMENT 2. Goodness of
data
Unit of analysis
Sampling Time Data-collection
(population to
design horizon method
be studied)
3. Hypotheses
Individuals Probability/ One-shot Interviewing testing
Dyads nonprobability (cross-sectional) Questionnaire
Groups Sample Longitudinal Observation
size (n)
Organizations
Unobtrusive
Machines methods
etc.
office table can be easily measured with a measuring tape or a ruler. The same
is true for measuring the office floor area. Data representing several demographic
characteristics of the office personnel are also easily obtained by asking employ-
ees simple, straightforward questions, as for example:
• How long have you been working in this organization?
• How long have you been working on this particular assignment?
• What is your job title?
• What is your marital status?
One can also check the company records to obtain or verify certain types of
information, as for example, the absenteeism of employees or their objective per-
formance in terms of the number of products produced or the rejects during the
course of each month. However, even such objective data might, in some cases,
call for careful interpretation while making managerial decisions. For example,
the decision to fire a factory worker would depend on whether he was respon-
sible for 10 rejects during a particular day because he was running a high fever
(one incident of a day’s bad work that was beyond the control of the worker),
or if he had 10 days of several instances of rejects over the course of a month
because he is just a slipshod worker (10 incidents of laxity). Here, the number
of incidents and the motivation of the worker are likely to play a part in deci-
sion making.