Page 61 - Cardiac Electrophysiology | A Modeling and Imaging Approach
P. 61
P. 61
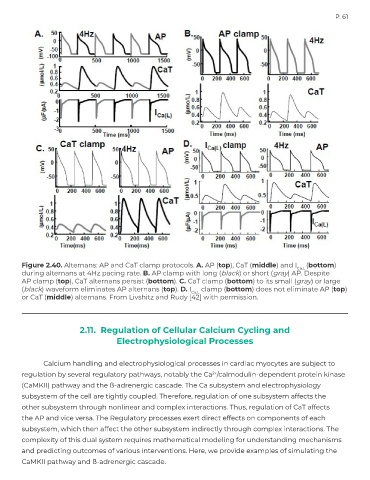
Figure 2.40. Alternans: AP and CaT clamp protocols. A. AP (top), CaT (middle) and I Ca,L (bottom)
during alternans at 4Hz pacing rate. B. AP clamp with long (black) or short (gray) AP. Despite
AP clamp (top), CaT alternans persist (bottom). C. CaT clamp (bottom) to its small (gray) or large
(black) waveform eliminates AP alternans (top). D. I Ca,L clamp (bottom) does not eliminate AP (top)
or CaT (middle) alternans. From Livshitz and Rudy [42] with permission.
2.11. Regulation of Cellular Calcium Cycling and
Electrophysiological Processes
Calcium handling and electrophysiological processes in cardiac myocytes are subject to
regulation by several regulatory pathways, notably the Ca /calmodulin-dependent protein kinase
2+
(CaMKII) pathway and the ß-adrenergic cascade. The Ca subsystem and electrophysiology
subsystem of the cell are tightly coupled. Therefore, regulation of one subsystem affects the
other subsystem through nonlinear and complex interactions. Thus, regulation of CaT affects
the AP and vice versa. The Regulatory processes exert direct effects on components of each
subsystem, which then affect the other subsystem indirectly through complex interactions. The
complexity of this dual system requires mathematical modeling for understanding mechanisms
and predicting outcomes of various interventions. Here, we provide examples of simulating the
CaMKII pathway and ß-adrenergic cascade.